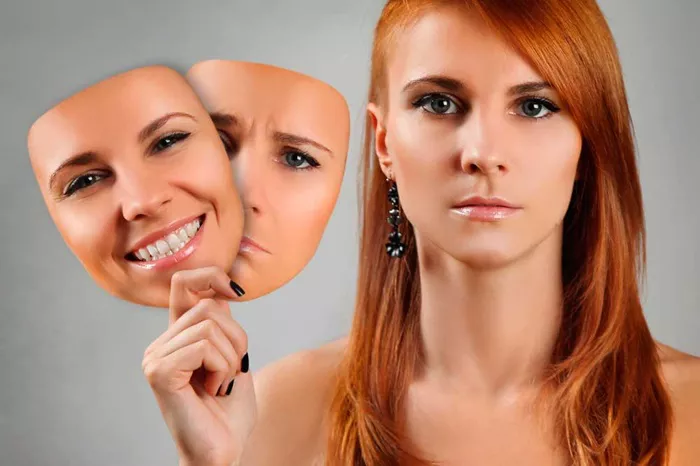
Bipolar disorder, characterized by extreme mood swings that include emotional highs (mania or hypomania) and lows (depression), can significantly impact a person’s life. However, with proper treatment and management, individuals with bipolar disorder can lead fulfilling lives. This article explores the limitations imposed by bipolar disorder and provides strategies to navigate these challenges effectively.
Understanding Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is a mental health condition that affects mood, energy levels, and the ability to function. The disorder is divided into several types, each with its own unique pattern of mood changes:
Bipolar I Disorder: Defined by manic episodes that last at least seven days or by manic symptoms that are severe enough to require immediate hospital care. Depressive episodes also occur and typically last at least two weeks.
Bipolar II Disorder: Characterized by a pattern of depressive episodes and hypomanic episodes, which are less severe than full-blown manic episodes.
Cyclothymic Disorder: Defined by periods of hypomanic symptoms as well as periods of depressive symptoms lasting for at least two years (one year in children and adolescents), but the symptoms do not meet the diagnostic requirements for a hypomanic episode and a depressive episode.
Impact on Daily Life
Bipolar disorder can affect various aspects of daily life, from personal relationships to professional responsibilities. The mood swings associated with the disorder can lead to unpredictable behavior and emotional instability, making certain activities particularly challenging.
Activities to Approach with Caution
Living with bipolar disorder means recognizing and respecting the limitations it imposes. While it is crucial to lead an active and engaged life, some activities require careful consideration and planning.
1. High-Stress Jobs
Stress is a significant trigger for mood episodes in individuals with bipolar disorder. High-stress jobs, characterized by long hours, tight deadlines, and high expectations, can exacerbate symptoms.
Impact: Stressful environments can trigger manic or depressive episodes, making it difficult to maintain stability.
Management Strategies: Opt for jobs with flexible hours, supportive work environments, and manageable stress levels. Communicate openly with employers about your condition and needs.
2. Irregular Sleep Patterns
Consistent sleep is crucial for managing bipolar disorder. Irregular sleep patterns, including staying up late or frequent time zone changes, can destabilize mood.
Impact: Lack of sleep can trigger manic episodes, while too much sleep can lead to depressive episodes.
Management Strategies: Establish a regular sleep routine, avoid caffeine and electronic devices before bed, and consider using sleep aids if recommended by a healthcare provider.
3. Substance Abuse
Alcohol and drugs can interact negatively with medications used to treat bipolar disorder and can exacerbate mood swings.
Impact: Substance abuse can impair judgment, worsen symptoms, and lead to dangerous behaviors during manic or depressive episodes.
Management Strategies: Avoid alcohol and drugs. Seek support through therapy, support groups, and lifestyle changes to maintain sobriety.
4. Financial Management
Manic episodes can lead to impulsive spending and poor financial decisions, while depressive episodes may result in neglecting financial responsibilities.
Impact: Financial instability can increase stress and contribute to further mood episodes.
Management Strategies: Create a budget, use financial tools to track spending, and consider appointing a trusted person to help manage finances during severe mood episodes.
Interpersonal Relationships
Bipolar disorder can strain personal relationships due to mood swings and unpredictable behavior. It’s important to manage these relationships carefully to maintain support and stability.
1. Romantic Relationships
Maintaining romantic relationships can be challenging due to the emotional highs and lows associated with bipolar disorder.
Impact: Partners may struggle to understand mood changes, leading to conflicts and misunderstandings.
Management Strategies: Open communication about the condition, couples therapy, and involving partners in treatment plans can help.
2. Family Dynamics
Family members may feel overwhelmed by the demands of supporting a loved one with bipolar disorder.
Impact: Family stress can exacerbate symptoms and create a cycle of emotional turbulence.
Management Strategies: Family therapy, education about the disorder, and creating a support network can alleviate stress and improve understanding.
3. Social Interactions
Social interactions can be challenging during both manic and depressive episodes. Manic episodes may lead to overly enthusiastic behavior, while depressive episodes can result in withdrawal.
Impact: Social instability can lead to isolation and loneliness, worsening the condition.
Management Strategies: Maintain a balance in social activities, communicate openly with friends about your needs, and avoid overcommitting.
Travel and Lifestyle Changes
Travel and significant lifestyle changes can disrupt routines, leading to increased stress and instability for those with bipolar disorder.
1. Frequent Travel
Frequent travel, especially across time zones, can disrupt sleep patterns and routines.
Impact: Disrupted routines can trigger mood episodes.
Management Strategies: Plan travel carefully, maintain regular sleep schedules, and have a support plan in place for managing symptoms while away from home.
2. Major Life Events
Events such as moving, changing jobs, or significant changes in personal relationships can be particularly stressful.
Impact: Major life events can destabilize mood and trigger episodes.
Management Strategies: Plan major changes carefully, seek support from healthcare providers, and have coping strategies in place.
Self-Care and Medication Management
Effective management of bipolar disorder relies heavily on self-care and adherence to treatment plans, including medication.
1. Medication Adherence
Skipping medications or not following the prescribed regimen can lead to mood destabilization.
Impact: Inconsistent medication use can result in severe mood episodes and decreased effectiveness of treatment.
Management Strategies: Set reminders, use pill organizers, and maintain regular appointments with healthcare providers to ensure adherence.
2. Self-Care Practices
Neglecting self-care can exacerbate symptoms and decrease overall well-being.
Impact: Poor self-care can lead to worsening of symptoms and decreased ability to cope with stress.
Management Strategies: Prioritize self-care activities such as regular exercise, healthy eating, and mindfulness practices.
Seeking and Utilizing Support
Support from healthcare providers, support groups, and loved ones is essential for managing bipolar disorder effectively.
1. Professional Support
Regular consultations with healthcare providers, including psychiatrists and therapists, are crucial.
Impact: Professional support helps manage symptoms, adjust medications, and provide coping strategies.
Management Strategies: Keep regular appointments, be open about symptoms, and follow treatment plans.
2. Support Groups
Connecting with others who have bipolar disorder can provide emotional support and practical advice.
Impact: Support groups offer understanding, reduce feelings of isolation, and share coping strategies.
Management Strategies: Join local or online support groups, participate regularly, and build a network of support.
Education and Advocacy
Educating oneself and others about bipolar disorder can reduce stigma and improve management.
1. Self-Education
Understanding bipolar disorder helps in recognizing symptoms and managing the condition effectively.
Impact: Better understanding leads to more effective self-management and communication with healthcare providers.
Management Strategies: Read reputable sources, attend workshops, and stay informed about the latest research and treatments.
2. Advocating for Understanding
Educating friends, family, and employers about bipolar disorder can create a more supportive environment.
Impact: Increased awareness and understanding reduce stigma and provide better support networks.
Management Strategies: Share information, speak openly about the condition, and advocate for mental health awareness.
Conclusion
Bipolar disorder imposes certain limitations, but with proper management, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Understanding and respecting these limitations, maintaining consistent routines, and seeking support are crucial. By prioritizing self-care, adhering to treatment plans, and leveraging support networks, those with bipolar disorder can navigate the challenges and live a balanced life. Educating oneself and others about the disorder further enhances the ability to manage it effectively, reducing stigma and fostering a supportive environment.
[inline_related_posts title=”You Might Be Interested In” title_align=”left” style=”list” number=”6″ align=”none” ids=”9315,9318,9247″ by=”categories” orderby=”rand” order=”DESC” hide_thumb=”no” thumb_right=”no” views=”no” date=”yes” grid_columns=”2″ post_type=”” tax=””]