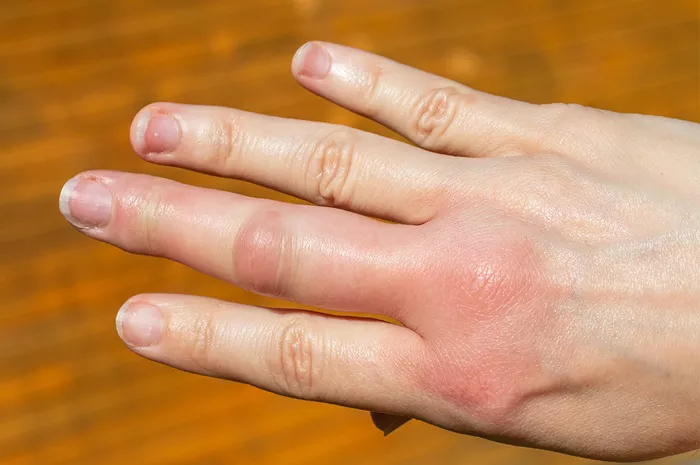
Bee stings are a common occurrence, especially during the warmer months when bees are most active. While most bee stings result in mild symptoms such as swelling and itching, some individuals may experience more severe allergic reactions that require immediate medical attention. In this article, we will explore the typical duration of swelling and itching from bee stings, factors that can affect recovery, and when to seek medical care.
The Bee Sting Experience
When a bee stings, it injects venom into the skin, which can trigger a range of reactions in the body. For most people, the initial sensation is a sharp pain followed by localized swelling, redness, and itching at the site of the sting. These symptoms are typically mild and subside within a few hours to a few days.
Duration of Swelling and Itching
The duration of swelling and itching from a bee sting can vary depending on several factors, including the individual’s sensitivity to bee venom, the location of the sting, and any pre-existing medical conditions. In general, mild swelling and itching from a bee sting typically resolve within 24 to 48 hours. However, in some cases, symptoms may persist for several days or even weeks, especially if the individual has an allergic reaction or experiences complications such as infection.
Factors Affecting Recovery
Several factors can affect the recovery time from bee sting swelling and itching:
Severity of Reaction: Individuals who have a mild allergic reaction to bee stings may experience more pronounced swelling and itching that lasts longer than those who have no allergies. Severe allergic reactions, known as anaphylaxis, can cause widespread swelling, hives, difficulty breathing, and other life-threatening symptoms that require immediate medical attention.
Location of the Sting: Bee stings on certain parts of the body, such as the face, neck, or genitals, may result in more significant swelling and discomfort due to the thinner skin and increased blood flow to these areas.
Treatment: Prompt treatment of a bee sting can help reduce swelling and itching and speed up recovery. Applying a cold compress, taking over-the-counter antihistamines or pain relievers, and using topical corticosteroids can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing.
Individual Factors: Factors such as age, overall health, and immune function can influence how quickly the body responds to a bee sting. Young children, older adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems may experience prolonged symptoms and slower recovery.
When to Seek Medical Care
While most bee stings cause mild symptoms that resolve on their own, certain situations warrant medical attention:
Severe Allergic Reaction: If you or someone else experiences symptoms of anaphylaxis, such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, rapid heartbeat, or dizziness, seek emergency medical care immediately. Anaphylaxis is a life-threatening condition that requires prompt treatment with epinephrine and other interventions.
Multiple Stings: Multiple bee stings can overwhelm the body’s immune system and lead to a more severe reaction, especially in individuals with allergies or other health conditions. If you are stung multiple times or experience symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or fainting, seek medical attention.
Infection: In some cases, bee stings can become infected if bacteria enter the skin through the sting site. Signs of infection include increasing redness, warmth, swelling, pain, or drainage of pus from the sting site. If you suspect that a bee sting has become infected, consult a healthcare provider for evaluation and treatment.
Persistent Symptoms: If swelling and itching from a bee sting persist for more than a few days or worsen over time, it’s a good idea to consult a healthcare provider. They can assess the sting site, provide appropriate treatment, and rule out any underlying complications.
Preventing Bee Stings
While bee stings are difficult to avoid entirely, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk:
Avoid Provoking Bees: Bees are most likely to sting when they feel threatened or agitated. Avoid swatting at bees or disturbing their nests, and be mindful of your surroundings when outdoors.
Wear Protective Clothing: When spending time outdoors, especially in areas where bees are common, wear light-colored clothing and avoid wearing floral patterns or strong fragrances that may attract bees. Consider wearing long sleeves, pants, and closed-toe shoes to minimize exposed skin.
Use Insect Repellent: Applying insect repellent containing DEET or picaridin can help deter bees and other stinging insects. Be sure to follow the instructions on the product label and reapply as needed.
Stay Calm and Still: If a bee approaches you, remain calm and still to avoid provoking it. Slowly move away from the bee without making sudden movements or swatting at it.
Seek Professional Removal: If you discover a bee nest or hive near your home or property, contact a pest control professional for safe and effective removal.
Conclusion
Swelling and itching from bee stings are common reactions that typically resolve within a few hours to a few days. However, the duration of symptoms can vary depending on individual factors and the severity of the reaction. While most bee stings can be managed at home with over-the-counter treatments, it’s important to seek medical attention if you experience signs of a severe allergic reaction, infection, or persistent symptoms. By taking precautions to avoid bee stings and knowing how to respond if stung, you can minimize your risk of complications and enjoy the great outdoors safely.
[inline_related_posts title=”You Might Be Interested In” title_align=”left” style=”list” number=”6″ align=”none” ids=”8709,8641,8649″ by=”categories” orderby=”rand” order=”DESC” hide_thumb=”no” thumb_right=”no” views=”no” date=”yes” grid_columns=”2″ post_type=”” tax=””]