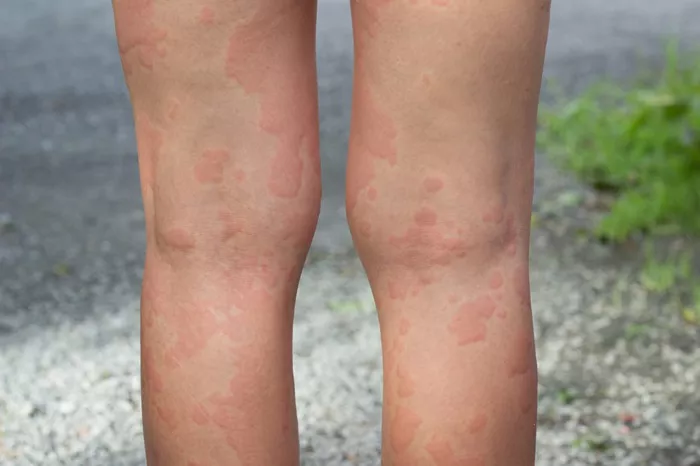
Viral hives, also known as viral urticaria or viral rash, are a common skin reaction that can occur in response to viral infections. These hives typically manifest as raised, red, and itchy welts on the skin and can be accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, fatigue, and body aches. While viral hives are usually self-limiting and resolve on their own, many individuals may wonder how long they can expect the hives to last and what steps they can take to manage symptoms. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the duration of viral hives, factors that influence their persistence, and strategies for symptom management and relief.
Understanding Viral Hives
Before discussing the duration of viral hives, it’s essential to understand what causes them. Viral hives are a type of allergic reaction that occurs when the body’s immune system releases histamine in response to a viral infection. The histamine causes blood vessels in the skin to leak, leading to the characteristic raised welts and itching associated with hives.
Viral hives can be triggered by a wide range of viral infections, including:
1. Common cold viruses (rhinovirus)
2. Influenza viruses
3. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
4. Herpes simplex virus (HSV)
5. Hepatitis viruses
6. HIV/AIDS
7. Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
8. Enteroviruses
9. Zika virus
10. Dengue virus
11. And many others
The appearance and severity of viral hives can vary depending on the underlying viral infection, the individual’s immune response, and other factors such as age, overall health, and genetics.
Duration of Viral Hives
The duration of viral hives can vary widely depending on several factors, including the underlying viral infection, the individual’s immune response, and the effectiveness of symptom management strategies. In general, viral hives tend to resolve on their own within a few days to a few weeks. However, some cases may persist for longer periods, particularly if the underlying viral infection is severe or chronic.
Common durations for viral hives include:
Acute Viral Hives: Acute viral hives typically last for a few days to a few weeks and are often associated with short-term viral infections such as the common cold or flu. Once the underlying viral infection resolves, the hives usually subside on their own.
Chronic Viral Hives: In some cases, viral hives may persist for longer periods, ranging from several weeks to several months or even longer. Chronic viral hives may be associated with chronic viral infections such as hepatitis or HIV/AIDS, or they may be triggered by recurrent viral infections or other underlying health conditions.
Intermittent Viral Hives: Some individuals may experience intermittent episodes of viral hives, where the hives come and go over time. These episodes may be triggered by recurrent viral infections, changes in the immune system, or other factors.
It’s important to note that the duration of viral hives can vary from person to person, and individual experiences may differ based on various factors such as the severity of symptoms, the effectiveness of treatment, and the presence of underlying health conditions.
Factors Influencing the Duration of Viral Hives
Several factors can influence the duration of viral hives, including:
Underlying Viral Infection: The type and severity of the underlying viral infection can impact the duration of viral hives. In general, acute viral hives associated with short-term infections tend to resolve more quickly than hives associated with chronic or recurring viral infections.
Immune Response: The individual’s immune response plays a significant role in determining the duration of viral hives. A robust immune response may help clear the viral infection more quickly and lead to faster resolution of hives, while a weakened or dysregulated immune response may prolong symptoms.
Treatment and Management: The effectiveness of treatment and symptom management strategies can also influence the duration of viral hives. Individuals who receive prompt medical care, follow recommended treatment protocols, and practice good self-care may experience faster relief from symptoms compared to those who do not seek treatment or experience delays in care.
Underlying Health Conditions: Underlying health conditions, such as allergies, autoimmune disorders, and chronic diseases, can impact the duration and severity of viral hives. Individuals with pre-existing health conditions may experience prolonged or more severe symptoms compared to those without underlying health issues.
Management and Relief of Viral Hives
While viral hives typically resolve on their own, there are several strategies that individuals can use to manage symptoms and promote relief:
Over-the-Counter Antihistamines: Antihistamine medications can help reduce itching and inflammation associated with viral hives. Over-the-counter options such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl), cetirizine (Zyrtec), and loratadine (Claritin) are commonly used to relieve hives symptoms. However, individuals should consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new medication, particularly if they have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
Topical Treatments: Calamine lotion, hydrocortisone cream, and other topical treatments can provide relief from itching and irritation associated with viral hives. Applying cool compresses or taking cool baths can also help soothe inflamed skin and reduce discomfort.
Avoid Triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers that may exacerbate viral hives can help prevent flare-ups and promote symptom relief. Common triggers include certain foods, medications, environmental allergens, stress, and temperature extremes.
Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water and staying hydrated can help support overall skin health and promote healing from viral hives. Avoiding alcohol and caffeine, which can dehydrate the body, may also be beneficial.
Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate symptoms of viral hives and other skin conditions. Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, and mindfulness can help reduce stress levels and promote overall well-being.
Seek Medical Care: Individuals experiencing severe or persistent symptoms of viral hives should seek medical care from a healthcare provider. A healthcare provider can perform a thorough evaluation, identify underlying causes or contributing factors, and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Follow-up Care: Follow-up care is essential for monitoring symptoms, tracking progress, and adjusting treatment as needed. Individuals should communicate openly with their healthcare providers and report any changes or concerns regarding their condition.
Conclusion
Viral hives are a common skin reaction that can occur in response to viral infections. While they typically resolve on their own within a few days to a few weeks, the duration of viral hives can vary depending on factors such as the underlying viral infection, immune response, and treatment effectiveness. By understanding the factors influencing the duration of viral hives and implementing appropriate management strategies, individuals can promote symptom relief, support skin health, and improve overall well-being. It’s essential for individuals experiencing severe or persistent symptoms of viral hives to seek medical care from a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and treatment. With proper care and management, most individuals can expect viral hives to resolve in a reasonable amount of time, allowing them to return to their daily activities with improved comfort and confidence.
[inline_related_posts title=”You Might Be Interested In” title_align=”left” style=”list” number=”6″ align=”none” ids=”8637,8555,8559″ by=”categories” orderby=”rand” order=”DESC” hide_thumb=”no” thumb_right=”no” views=”no” date=”yes” grid_columns=”2″ post_type=”” tax=””]