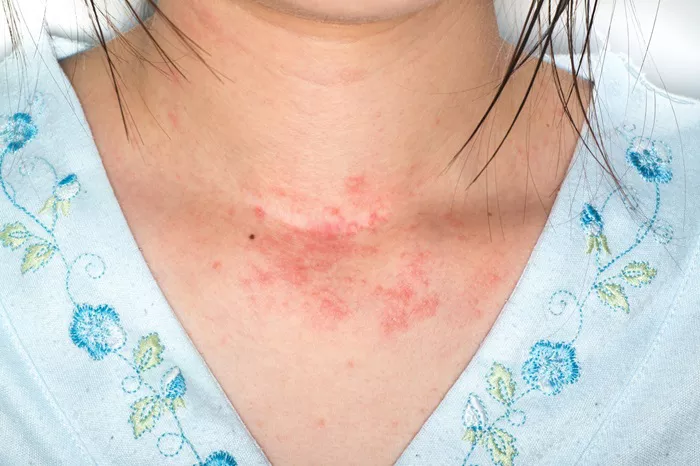
Allergic reactions on the skin, commonly known as skin allergies, can be uncomfortable, unsightly, and distressing. These reactions occur when the immune system responds to a harmless substance as though it were a threat. Skin allergies can manifest in several ways, such as hives, eczema, and contact dermatitis. Understanding the underlying causes, symptoms, and effective treatments can significantly help manage and alleviate these conditions.
Understanding Skin Allergic Reactions
Skin allergic reactions are the result of the body’s immune system reacting to an allergen. These reactions can be caused by a variety of substances including foods, medications, plants, chemicals, and animal dander. The symptoms and severity of skin allergies can vary widely among individuals.
Common Types of Skin Allergic Reactions
Contact Dermatitis: This occurs when the skin comes into contact with an allergen or an irritant. Common culprits include nickel, latex, and poison ivy.
Hives (Urticaria): These are red, itchy welts that can occur as a result of an allergic reaction to medication, foods, and infections.
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis): Often linked to a combination of genetic and environmental factors, eczema is characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin.
Identifying the Allergens
Determining the specific allergen causing the reaction is a critical step in managing skin allergies. Allergens can be identified through:
Patch Testing: Used primarily for diagnosing contact dermatitis. Small amounts of various substances are applied to the skin and monitored for reactions.
Skin Prick Testing: This can help identify allergies to airborne substances, foods, and more.
Immediate Treatments for Skin Allergic Reactions
Cold Compresses: Applying a cold compress to the affected area can help reduce swelling and soothe itching.
Topical Steroids: Creams and ointments containing steroids can reduce inflammation and are particularly effective for contact dermatitis and eczema.
Antihistamines: Oral or topical antihistamines can help control the histamine response that contributes to itching and swelling.
Prescription Treatments
When over-the-counter treatments are insufficient, prescription medications may be necessary:
Corticosteroids: For severe flare-ups, stronger corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce symptoms.
Immunomodulators: Medications like tacrolimus and pimecrolimus can be used to control inflammation and are especially useful for long-term management of eczema.
Biologic Drugs: Newer treatments for severe eczema include biologic drugs that target specific parts of the immune system.
Natural Remedies and Alternative Treatments
Many individuals find relief using natural and alternative remedies:
Oatmeal Baths: Colloidal oatmeal has properties that soothe itching and inflammation.
Coconut Oil: Known for its moisturizing and anti-inflammatory properties, it can be beneficial for dry, itchy skin associated with eczema.
Aloe Vera: This plant is renowned for its healing and soothing properties and can be applied directly to the affected area.
Long-Term Management Strategies
Managing skin allergies often requires ongoing strategies to prevent flare-ups:
Moisturizing Regularly: Keeping the skin moisturized helps prevent dryness and irritation. Choosing hypoallergenic and fragrance-free moisturizers is crucial.
Avoiding Known Allergens: Once allergens are identified, avoiding them can prevent reactions.
Dietary Management: If food allergies are involved, modifying the diet accordingly can help manage symptoms.
Lifestyle Modifications
Simple changes in daily habits can have a significant impact on managing skin allergies:
Clothing Choices: Wearing clothes made of natural fibers like cotton can prevent irritation.
Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate allergic reactions, so incorporating stress-reduction techniques like yoga and meditation can be beneficial.
Home Environment: Reducing allergens at home by using air purifiers and hypoallergenic bedding can also help.
When to See a Dermatologist
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider if:
Symptoms Persist or Worsen: If over-the-counter treatments do not alleviate symptoms or if symptoms worsen, seeing a dermatologist is recommended.
Signs of Infection: If the skin becomes overly red, warm, or pus begins to form, these could be signs of an infection that requires medical attention.
Conclusion: A Comprehensive Approach to Managing Skin Allergies
Effectively managing skin allergic reactions involves a combination of identifying triggers, applying appropriate treatments, and making lifestyle adjustments. Whether through medical treatments, natural remedies, or preventive measures, individuals can achieve substantial relief from symptoms and improve their quality of life. Ultimately, the best approach depends on the individual’s specific circumstances and should be guided by a healthcare professional to ensure both safety and efficacy.
[inline_related_posts title=”You Might Be Interested In” title_align=”left” style=”list” number=”6″ align=”none” ids=”8299,8296,8292″ by=”categories” orderby=”rand” order=”DESC” hide_thumb=”no” thumb_right=”no” views=”no” date=”yes” grid_columns=”2″ post_type=”” tax=””]