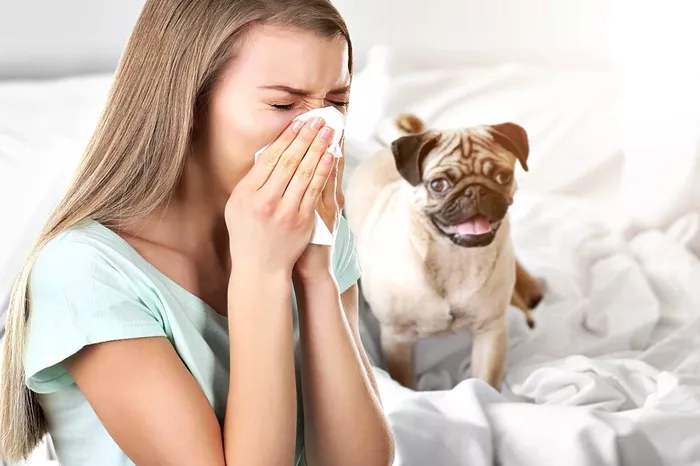
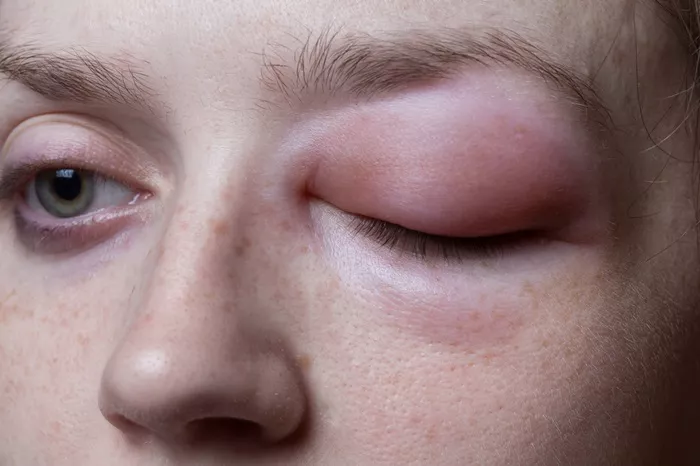
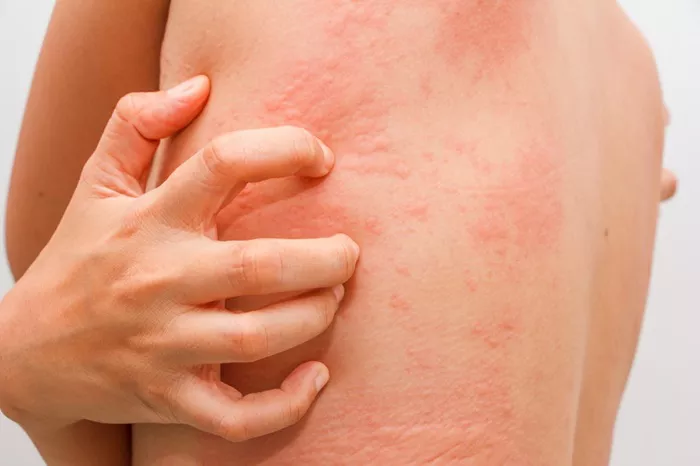
Swollen eyes are a common symptom experienced by individuals suffering from allergies. This condition, often accompanied by redness, itching, and watering, can cause significant discomfort and interfere with daily activities. This article will explore the causes of allergy-induced swollen eyes, the best treatment options available, and effective prevention strategies to help manage this bothersome symptom.
Allergy-Induced Swollen Eyes
Allergies occur when the immune system reacts to a foreign substance, such as pollen, pet dander, or dust mites, that it considers harmful. This reaction can lead to various symptoms, one of which is swollen eyes. This condition, medically known as allergic conjunctivitis, affects the conjunctiva, the clear layer of tissue lining the inside surface of the eyelid and the white part of the eyeball.
Identifying the Allergens
Common Environmental Allergens: The most frequent causes of allergy-induced swollen eyes are environmental allergens. These include pollen from trees, grasses, and weeds; dust mites; pet dander; and molds. Identifying the specific allergen causing the reaction is crucial for effective treatment and prevention.
Food Allergens and Additives: Though less common, certain foods and additives can also lead to swollen eyes as part of a broader allergic reaction. Common culprits include nuts, dairy, shellfish, and food preservatives like sulfites.
Symptoms Associated with Allergic Swollen Eyes
Allergy-induced swollen eyes can manifest several symptoms, which may vary in intensity from person to person. Key symptoms include:
Redness: The eyes may appear redder than usual due to inflammation.
Itchiness: This can range from mild to severe and often accompanies swelling.
Tearing: Excessive tear production is a common response to allergens.
Discharge: Some individuals may notice a clear or slightly thick, whitish discharge.
Photophobia: Sensitivity to light is not uncommon.
Understanding these symptoms is essential for diagnosing and treating allergic conjunctivitis effectively.
Initial Steps in Treating Allergy-Induced Swollen Eyes
Cold Compresses: Applying a cold compress can help reduce swelling and soothe irritated eyes. This method contracts blood vessels, thereby decreasing inflammation and redness.
Hygiene and Environment Control: Keeping the environment free of allergens can significantly reduce symptoms. Regular cleaning to remove dust, using air purifiers, and avoiding known triggers are effective strategies.
Over-the-Counter Solutions
Antihistamine Eye Drops: These can quickly relieve symptoms like itchiness and swelling. They work by blocking histamine, a compound released by the immune system during an allergic reaction.
Artificial Tears: Lubricating eye drops can help flush out allergens from the eyes and provide moisture, relieving symptoms of dryness and irritation.
Oral Antihistamines: These medications can help manage more widespread symptoms of allergies, including swollen eyes, especially when the trigger is not easily avoidable.
Prescription Treatments
For severe cases, prescription medications may be necessary:
Anti-inflammatory Eye Drops: Steroid eye drops are sometimes prescribed for short-term use to quickly reduce inflammation.
Immunotherapy: In cases where allergens cannot be easily avoided, such as pollen, immunotherapy or allergy shots might be recommended. This treatment involves regular injections of the allergen, with the aim of desensitizing the body’s immune response over time.
Home Remedies and Natural Treatments
Tea Bags: Applying chilled tea bags to the eyes can help reduce swelling due to the anti-inflammatory properties of tea.
Essential Oils: Certain oils, like chamomile and lavender, have anti-inflammatory properties. However, they should be used cautiously and never applied directly to the eyes or eyelids.
Dietary Adjustments: Increasing intake of omega-3 fatty acids and flavonoids through diet can support eye health and reduce inflammation.
Long-Term Management Strategies
Allergen Avoidance: The most effective long-term strategy is to avoid allergens. This might involve staying indoors during high pollen counts or removing pets from the home.
Regular Cleaning: Reducing dust and mold in the home can help minimize exposure to these common triggers.
Monitoring Pollen Counts: Keeping track of pollen forecasts can help individuals with seasonal allergies take preventative measures before symptoms start.
When to See a Doctor
It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional if:
Symptoms Persist or Worsen: If swelling does not improve with home treatment or over-the-counter remedies.
Vision is Affected: Any changes in vision during an allergic reaction should be promptly evaluated.
Signs of Infection: If symptoms include severe pain, fever, or pus discharge.
Conclusion: Achieving Relief from Allergy-Induced Swollen Eyes
Managing and treating allergy-induced swollen eyes involves a combination of identifying triggers, applying immediate remedies, and implementing long-term strategies to reduce exposure to allergens. Over-the-counter medications and home remedies can effectively manage mild symptoms, while more persistent cases may require professional medical treatment. By understanding the underlying causes and appropriate treatment options, individuals suffering from allergic swollen eyes can achieve significant relief and improve their quality of life.
[inline_related_posts title=”You Might Be Interested In” title_align=”left” style=”list” number=”6″ align=”none” ids=”8283,8161,8158″ by=”categories” orderby=”rand” order=”DESC” hide_thumb=”no” thumb_right=”no” views=”no” date=”yes” grid_columns=”2″ post_type=”” tax=””]