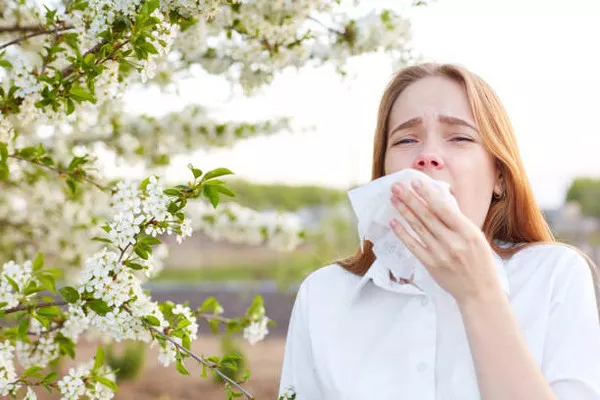
Pollen allergies, commonly referred to as hay fever or allergic rhinitis, affect millions of individuals worldwide. Each year, as plants release pollen grains into the air to fertilize other plants, many people experience a range of symptoms triggered by their immune system’s response to these harmless substances. Although pollen allergies are widely recognized, the breadth and impact of their side effects can vary significantly, affecting daily functioning and quality of life. This article delves into the nature of pollen allergies, the symptoms they trigger, secondary effects, and their broader impacts on health.
What are Pollen Allergies?
Pollen allergies occur when the immune system mistakenly identifies pollen as a harmful invader, triggering a series of immune responses that aim to attack and eliminate the perceived threat. This allergic reaction is primarily caused by the inhalation of pollen grains, which come from a variety of plants, including trees, grasses, and weeds.
Primary Symptoms of Pollen Allergies
The immediate symptoms of pollen allergies are well-known and can range from mild to severe, depending on the individual’s sensitivity and the pollen count in the environment. These symptoms are the body’s immediate response to pollen exposure and include:
Nasal Congestion: Swelling of the nasal passages, making breathing through the nose difficult.
Runny Nose: Increased mucus production leads to a clear, water-like nasal discharge.
Itchy, Watery Eyes: Pollen exposure can cause inflammation in the eyes, leading to redness, itching, and excessive tear production.
Sneezing: Sudden, frequent, uncontrollable bursts of sneezing are a direct reaction to irritation in the nasal passages.
Itchy Throat or Mouth: Sensations of itchiness or irritation in the throat or mouth are common.
Sinus Pressure: Swelling in the sinus cavities can create feelings of pressure or pain in the face.
Decreased Sense of Smell or Taste: Nasal congestion and inflammation can temporarily impair these senses.
These primary symptoms can be bothersome on their own, but the secondary effects and complications that arise from pollen allergies can also significantly affect an individual’s well-being.
Secondary Effects and Complications of Pollen Allergies
While the immediate symptoms of pollen allergies are typically manageable with over-the-counter medications and lifestyle adjustments, the condition can lead to more severe secondary effects and complications if not properly treated:
Poor Sleep Quality: Nasal congestion and sinus pressure can make it difficult to breathe at night, leading to disrupted sleep and daytime fatigue.
Chronic Sinusitis: Persistent or recurrent nasal congestion and sinus pressure can lead to sinusitis, an inflammation or infection of the sinus cavities.
Asthmatic Responses: In some individuals, pollen allergies can trigger asthma symptoms, such as wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing.
Ear Infections: Eustachian tube dysfunction caused by nasal congestion can lead to a buildup of fluid in the middle ear, creating a breeding ground for bacteria and potential infections.
Impaired Daily Functioning: The cumulative effect of symptoms can impair cognitive functions, leading to decreased concentration, attention deficits, and reduced productivity.
Emotional and Psychological Impact: Chronic discomfort and sleep disruption may contribute to mood disorders such as depression or anxiety.
Managing and Treating Pollen Allergies
Effective management and treatment of pollen allergies are crucial in reducing both primary symptoms and secondary effects. Treatment strategies include:
Avoidance of Pollen Exposure: Staying indoors on days with high pollen counts, using air purifiers, and keeping windows closed can reduce exposure.
Pharmacotherapy: Over-the-counter antihistamines, decongestants, and nasal corticosteroids can effectively reduce symptoms.
Immunotherapy: Allergy shots or sublingual tablets can help the body build tolerance to pollen, potentially reducing the severity of allergic reactions over time.
Nasal Irrigation: Using saline solutions to flush out the nasal passages can alleviate congestion and remove irritants.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatments, certain lifestyle adjustments and home remedies can help alleviate the symptoms of pollen allergies:
Regular Cleaning: Regularly cleaning the home, especially bedding and upholstered furniture, can reduce pollen accumulation.
Dietary Adjustments: Consuming a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fruits, and vegetables can support immune function and reduce inflammation.
Hydration: Increasing fluid intake can help thin mucus secretions, easing nasal congestion.
Conclusion
Pollen allergies are a significant source of discomfort and disruption for many individuals, with effects that can extend beyond simple allergic reactions to impacting overall health and quality of life. Understanding the full spectrum of symptoms and effects is crucial for those affected to take proactive steps in managing their condition. With appropriate strategies, both medical and lifestyle-oriented, individuals can minimize the impact of pollen allergies and maintain a high quality of life during allergy season.
[inline_related_posts title=”You Might Be Interested In” title_align=”left” style=”list” number=”6″ align=”none” ids=”8071,8063,7987″ by=”categories” orderby=”rand” order=”DESC” hide_thumb=”no” thumb_right=”no” views=”no” date=”yes” grid_columns=”2″ post_type=”” tax=””]