Pollen allergies, often referred to as seasonal allergic rhinitis or hay fever, affect millions of people worldwide. These allergies occur when an individual’s immune system reacts to pollen from trees, grasses, and weeds, treating it as a threat and triggering allergic reactions. This article explores the variety of medications available for managing pollen allergies, detailing their mechanisms, effectiveness, and suitability for different types of sufferers.
Understanding Pollen Allergies
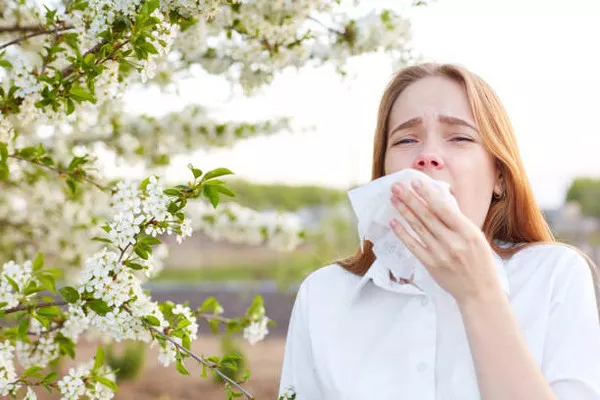
Before delving into treatments, it’s crucial to understand what pollen allergies entail and how they affect individuals. Pollen is a fine powder released by plants as part of their reproductive cycle, easily dispersed by wind. For sensitive individuals, this pollen triggers an immune response that can cause symptoms ranging from mild to debilitating.
Symptoms of Pollen Allergies
Typical symptoms of pollen allergies include:
1. Sneezing
2. Runny or stuffy nose
3. Itchy, watery eyes
4. Itchy throat or ear canals
5. Postnasal drip
6. Cough
Understanding these symptoms is crucial as they directly influence the choice of allergy medication.
Overview of Allergy Medications
A wide range of medications is available to treat pollen allergies. These can be categorized into several types, each with specific functions and benefits.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines are perhaps the most well-known type of allergy medication. They work by blocking histamine, a substance in the body that causes many of the symptoms of allergies.
Types of Antihistamines:
First-Generation Antihistamines: Such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl). These medications can be very effective but often cause drowsiness and other side effects.
Second-Generation Antihistamines: Including loratadine (Claritin), cetirizine (Zyrtec), and fexofenadine (Allegra). These are preferred for their fewer sedative effects and longer-lasting relief.
Corticosteroids
Nasal corticosteroids are considered by many experts to be among the most effective treatment options for nasal allergy symptoms. They reduce inflammation in the nasal passages, relieving congestion, sneezing, and an itchy or runny nose.
Commonly Used Corticosteroids Include:
1. Fluticasone (Flonase)
2. Budesonide (Rhinocort)
3. Mometasone (Nasonex)
Decongestants
Decongestants are used for short-term relief of nasal congestion. They work by narrowing blood vessels to reduce swelling and congestion in the nasal passages.
Types of Decongestants:
1. Pseudoephedrine (Sudafed)
2. Phenylephrine (available in many combination allergy medications)
It’s important to use decongestants cautiously as they can increase blood pressure and cause other side effects.
Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists
These medications block the action of leukotrienes, another group of chemicals involved in the allergic response. Montelukast (Singulair) is a commonly prescribed leukotriene receptor antagonist that can help manage nasal congestion, itchy eyes, and other symptoms.
Mast Cell Stabilizers
Mast cell stabilizers prevent the release of histamine and other chemicals from mast cells in the body. These medications are often used to prevent allergic symptoms before they start.
Examples Include:
Cromolyn sodium (NasalCrom), available as a nasal spray.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy can be a long-term solution for severe allergy sufferers. This treatment involves regular injections of purified allergen extracts to gradually desensitize the body’s immune system to pollen.
Combination Therapies
In some cases, a combination of medications may be recommended to manage symptoms effectively. For example, an antihistamine together with a nasal corticosteroid can provide relief from multiple symptoms.
Choosing the Right Medication
Factors to Consider
The best allergy medication for pollen depends on several factors, including:
1. Severity of symptoms
2. Specific symptoms (e.g., nasal congestion versus itchy eyes)
3 Individual health conditions (such as asthma or high blood pressure)
4. Age
5. Preferences regarding form of medication (e.g., pill vs. nasal spray)
Personalization of Treatment
Allergy treatments should be personalized. What works well for one person might not work for another. It’s often necessary to try different medications to find the most effective ones.
Expert Recommendations and Guidelines
Guidelines from Health Organizations
Leading health organizations often publish guidelines to help both patients and healthcare providers choose the most effective treatments for seasonal allergies. These guidelines typically recommend starting with nasal corticosteroids for nasal symptoms and considering antihistamines for broader allergy symptoms.
Consultation with Allergists
For those who struggle to manage their allergy symptoms, consultation with an allergist might be beneficial. Allergists can provide testing and tailored treatment plans, which might include immunotherapy.
Managing Pollen Exposure
While medication is important, managing exposure to pollen can also significantly reduce symptoms.
Effective Strategies Include:
1. Monitoring pollen counts and staying indoors on high pollen days.
2. Using air purifiers at home.
3. Keeping windows closed during pollen season.
4. Showering after returning indoors to remove pollen from hair and skin.
Conclusion
Pollen allergies can significantly impact quality of life, but with the right approach, symptoms can be effectively managed. The best medication for pollen allergies varies depending on individual symptoms, severity, and personal health. By understanding the available medications and how they work, individuals suffering from pollen allergies can find relief and return to their daily activities with minimal disruption.
Through a combination of the right medications, avoidance strategies, and possibly immunotherapy, those affected by pollen allergies can look forward to a season with fewer symptoms and greater comfort. Always consult healthcare providers to tailor a treatment plan that fits personal health profiles and allergy patterns.
[inline_related_posts title=”You Might Be Interested In” title_align=”left” style=”list” number=”6″ align=”none” ids=”8063,7987,7944″ by=”categories” orderby=”rand” order=”DESC” hide_thumb=”no” thumb_right=”no” views=”no” date=”yes” grid_columns=”2″ post_type=”” tax=””]