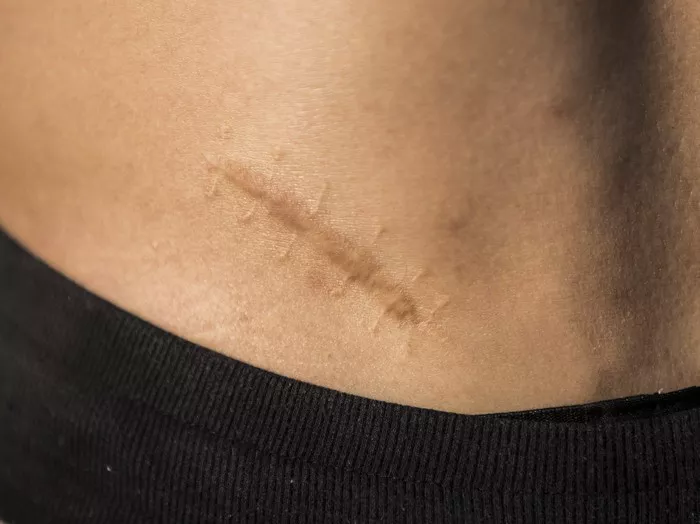
Scarring is a natural part of the healing process following surgery. It occurs as the body repairs the skin and tissue damage inflicted by surgical incisions. While some scarring is inevitable, the extent and appearance of these scars can vary widely among individuals due to factors such as genetics, the nature of the surgical cut, and the care taken during the healing process. For many, reducing the visibility and texture of scars is a priority post-surgery. This comprehensive article explores effective strategies to minimize scarring, enhance healing, and improve cosmetic outcomes.
Understanding Scarring: The Healing Process Explained
To effectively manage and reduce scarring, it’s essential to understand the physiological process behind wound healing, which can be divided into three phases:
Inflammatory Phase: This initial phase begins immediately after the incision is made. The body’s immune system responds by sending white blood cells to the area to combat bacteria and remove debris. This phase lasts for a few days and is characterized by redness, warmth, swelling, and sometimes pain.
Proliferative Phase: Lasting several weeks, this phase involves the growth of new tissue and blood vessels to replace those damaged by surgery. Collagen, a protein that gives skin its strength and structure, is produced in large amounts, leading to the formation of new tissue known as granulation tissue.
Maturation Phase: This is the longest phase, potentially lasting for several months to years. During this time, the body remodels the scar, improving its strength and appearance. The collagen that was rapidly laid down in the proliferative phase is realigned and matures, and the blood vessels in the area reduce, making the scar less noticeable.
Pre-Surgical Strategies to Reduce Scarring
Preparation before surgery can significantly influence the healing process and the development of scars. Consider the following strategies:
Choosing the Right Surgeon: Select a skilled surgeon familiar with advanced techniques that minimize tissue trauma and optimize the placement and size of incisions. Techniques such as minimally invasive surgery can result in smaller scars.
Discuss Incision Options: Depending on the type of surgery, there may be options for the placement of incisions that can minimize visible scarring. For example, incisions placed in less visible areas or along natural skin lines and creases can reduce the noticeable effects of scarring.
Pre-Surgical Skin Care: Optimizing skin health before surgery can improve outcomes. Hydrated, healthy skin tends to heal better. Nutrition plays a crucial role, with a balanced diet rich in vitamins C and E, zinc, and protein supporting skin health.
Post-Surgical Care for Minimizing Scarring
After surgery, how you care for your wound can impact the severity of scarring:
Follow Surgeon’s Instructions: Adhering strictly to your surgeon’s guidelines on wound care is crucial. This includes keeping the wound clean, applying prescribed topical treatments, and covering the wound if recommended.
Proper Wound Care: Initially, keeping the wound moist can prevent the formation of a hard scab, which can intensify scarring. Using petroleum jelly and a non-stick bandage can help.
Avoid Stress on the Wound: Physical stress on the healing incision can increase scar size. Avoid stretching, pulling, or exerting pressure on the affected area.
Advanced Wound Care Techniques
Technological and medical advancements have introduced several effective treatments for minimizing scars:
Silicone Gel Sheets: These sheets provide a protective layer over the scar, maintaining hydration and encouraging organized collagen formation. Studies have shown that silicone gel sheets can reduce scar thickness and discoloration.
Steroid Applications and Injections: These can be used to reduce collagen formation in overly active scars, such as hypertrophic scars and keloids, thus minimizing their appearance.
Laser Therapy: Various types of lasers can be used to reduce scar redness, improve skin texture, and encourage the remodeling of collagen. Laser therapy is often used for scars that do not respond well to more conventional treatments.
Nutrition and Lifestyle Factors Affecting Scar Healing
A holistic approach to health can influence the body’s ability to heal and reduce scarring:
Nutritional Support: A diet high in vitamins (A, C, E) and minerals (zinc, selenium) along with protein is crucial. These nutrients are vital for skin regeneration and collagen formation.
Hydration: Keeping the body well-hydrated helps maintain skin elasticity and strength, aiding the healing process.
Smoking and Alcohol Consumption: Both can impair wound healing and should be avoided post-surgery. Smoking decreases blood flow to the skin, delaying healing and potentially worsening scars.
Psychological Impact of Scarring
The appearance of scars can also impact a person’s mental health. It is important to address any concerns with your healthcare provider who may recommend:
Counseling: Talking with a therapist can help manage negative feelings associated with scarring.
Support Groups: Connecting with others who have experienced similar issues can provide emotional support and practical advice on managing scars.
Conclusion
Reducing scarring after surgery involves a combination of pre-surgical preparation, diligent post-surgical care, and the use of advanced treatments and technologies. A holistic approach, including proper nutrition and lifestyle adjustments, also plays a crucial role in the healing process. By understanding the science of scarring and actively engaging in recommended practices, patients can significantly improve their surgical outcomes and reduce the appearance of scars.
[inline_related_posts title=”You Might Be Interested In” title_align=”left” style=”list” number=”6″ align=”none” ids=”7962,7900,7808″ by=”categories” orderby=”rand” order=”DESC” hide_thumb=”no” thumb_right=”no” views=”no” date=”yes” grid_columns=”2″ post_type=”” tax=””]