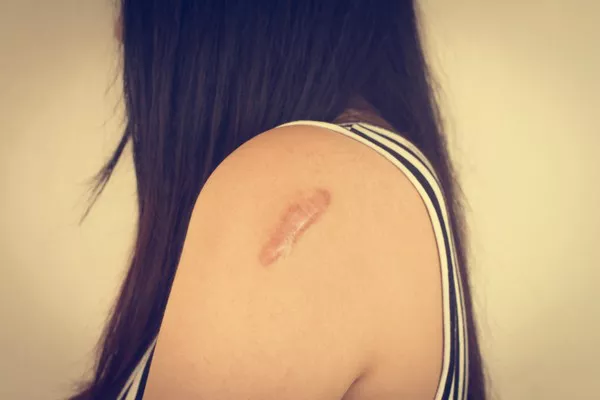
Bruising, also known as contusion, occurs when blood vessels underneath the skin are damaged, leading to leakage of blood into the surrounding tissues. This leakage results in discoloration of the skin, typically appearing as purple, blue, or blackish marks. While bruises are often harmless and resolve on their own over time, frequent or severe bruising may indicate underlying health issues or nutritional deficiencies.
Vitamins and Their Potential Benefits
Vitamin C: Enhancing Collagen Synthesis
Vitamin C plays a crucial role in collagen synthesis, a protein essential for maintaining the integrity of blood vessels and skin. Adequate vitamin C levels support the strength and resilience of blood vessel walls, reducing the likelihood of vessel damage and subsequent bruising. Citrus fruits, strawberries, kiwi, and bell peppers are excellent sources of vitamin C.
Vitamin K: Supporting Blood Clotting
Vitamin K is essential for proper blood clotting, helping to stop bleeding and promote wound healing. By facilitating the activation of clotting factors, vitamin K may reduce excessive bruising and accelerate the resolution of bruises. Leafy green vegetables, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and fermented foods like sauerkraut are rich sources of vitamin K.
Vitamin D: Promoting Bone and Muscle Health
While vitamin D‘s direct role in bruising prevention is less clear, it plays a crucial role in bone health and muscle function. Strong bones and muscles are less prone to injury, reducing the risk of bruising from falls or trauma. Sunlight exposure, fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and mushrooms are primary sources of vitamin D.
Bioflavonoids: Strengthening Blood Vessels
Bioflavonoids, natural compounds found in fruits, vegetables, and herbs, have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that may strengthen blood vessels and reduce capillary fragility. Foods rich in bioflavonoids include citrus fruits, berries, onions, and green tea.
Supplementation Considerations
Consultation with Healthcare Professionals
Before initiating any new supplements, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional, particularly if you’re taking medications or have existing health conditions. Certain vitamins, such as vitamin K, can interact with blood-thinning medications, potentially affecting clotting function.
Individual Needs
Individual vitamin requirements vary based on factors such as age, gender, overall health, and dietary habits. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides essential nutrients for overall health, including skin and blood vessel integrity.
Quality of Supplements
When selecting vitamin supplements, choose products from reputable brands that undergo rigorous testing for quality and purity. Look for certifications from independent organizations like the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) or NSF International to ensure product safety and efficacy.
Other Factors Contributing to Bruising
Medications
Certain medications, such as anticoagulants (blood thinners), antiplatelet drugs, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin, can increase the risk of bruising by impairing blood clotting function. If you’re taking these medications, discuss bruising concerns with your healthcare provider.
Medical Conditions
Medical conditions that affect blood clotting or weaken blood vessels, such as hemophilia, von Willebrand disease, or vitamin deficiencies (e.g., vitamin C or vitamin K deficiency), can contribute to easy bruising. Proper diagnosis and management of underlying conditions are essential for addressing bruising issues.
Aging
As we age, the skin becomes thinner and loses its elasticity, making it more susceptible to bruising. Additionally, age-related changes in blood vessel structure and function can increase the risk of capillary fragility and bruising. Taking preventive measures and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help minimize bruising risk in older adults.
Lifestyle and Prevention: Empowering Strategies
Protective Measures
Taking proactive steps to prevent injuries can significantly reduce the risk of bruising. Avoiding activities that pose a high risk of falls or trauma, wearing protective gear during sports or recreational activities, and exercising caution when handling sharp objects can help prevent bruises.
Healthy Lifestyle Habits
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can support overall well-being and reduce the risk of bruising. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, regular exercise to maintain muscle strength and flexibility, adequate hydration, and quality sleep are essential components of a healthy lifestyle. Managing stress and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption also contribute to skin health and resilience.
In conclusion, while vitamins play a role in preventing bruising, blood clotting, and overall health, there is no magic pill for preventing bruising. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and protective measures are key components of bruising prevention. By prioritizing a healthy lifestyle and seeking guidance from healthcare professionals, individuals can optimize their vitamin intake and reduce the risk of bruising.
[inline_related_posts title=”You Might Be Interested In” title_align=”left” style=”list” number=”6″ align=”none” ids=”6992,6917,6914″ by=”categories” orderby=”rand” order=”DESC” hide_thumb=”no” thumb_right=”no” views=”no” date=”yes” grid_columns=”2″ post_type=”” tax=””]