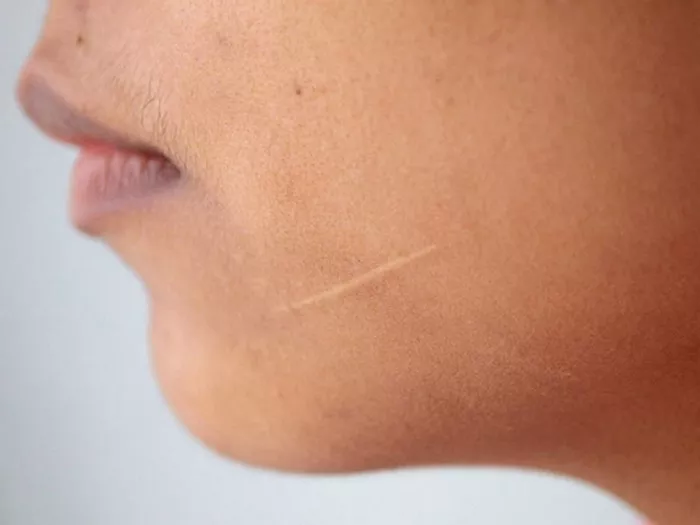
Scars, though often regarded as symbols of resilience and healing, can sometimes pose challenges beyond their physical appearance. Among the various types of scars, white scars stand out for their lack of pigmentation, which can be a source of self-consciousness and concern for many individuals. In this article, we embark on a journey to explore natural methods for repigmenting white scars, aiming to empower individuals with knowledge and strategies to support their skin’s natural healing process.
Understanding White Scars: Unveiling the Causes
White scars, also known as hypopigmented scars, are characterized by their pale or whitish appearance, resulting from a deficiency in melanin production within the scar tissue. Several factors contribute to the development of white scars, including:
Trauma or Injury: White scars often form in response to traumatic injuries, such as cuts, burns, or surgical incisions, where the skin’s natural pigment-producing cells, known as melanocytes, are damaged or destroyed.
Inflammation and Healing Process: The body’s inflammatory response to injury can disrupt the normal process of melanin production, leading to the formation of white scar tissue as the wound heals.
Skin Type and Genetics: Individual differences in skin type and genetics can influence the likelihood of developing white scars. People with lighter skin tones are more prone to hypopigmentation, although white scars can occur in individuals of any ethnic background.
Natural Repigmentation Methods: Harnessing the Power of Nature
While white scars may seem stubborn at first glance, there are several natural remedies and techniques that may help stimulate melanin production and reduce their appearance. Let’s explore some of these methods in detail:
Sun Exposure: The Double-Edged Sword
Sun exposure is a widely discussed topic in the context of scar healing and repigmentation. While controlled sun exposure can stimulate melanin production and help blend white scars with surrounding skin, it’s essential to approach this method with caution:
Benefits: Controlled exposure to sunlight can trigger the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin coloration, leading to gradual repigmentation of white scars. Additionally, sunlight exposure can promote vitamin D synthesis and overall skin health.
Risks: Excessive or unprotected sun exposure can cause sunburn, skin damage, and potentially worsen the appearance of scars. Individuals with sensitive skin or a history of skin cancer should exercise caution and consult a dermatologist before attempting sun exposure as a repigmentation method.
Natural Oils and Butters: Nourishing the Skin
Natural oils and butters have long been used in skincare for their moisturizing and nourishing properties. When applied topically to white scars, certain oils may help promote skin health and support the body’s natural healing process:
Coconut Oil: Known for its moisturizing and anti-inflammatory properties, coconut oil may help soften scar tissue and improve skin texture. However, its effectiveness in repigmenting white scars remains anecdotal, and results may vary depending on individual skin type and scar characteristics.
Shea Butter: Rich in vitamins and fatty acids, shea butter is prized for its moisturizing and emollient properties. When applied regularly to white scars, shea butter may help improve skin elasticity and texture, although its ability to repigment scars is limited.
Rosehip Oil: Packed with antioxidants and essential fatty acids, rosehip oil is renowned for its skin-rejuvenating properties. While it may help promote overall skin health and reduce the appearance of scars, its efficacy in repigmenting white scars remains uncertain.
Aloe Vera: Nature’s Soothing Balm
Aloe vera, derived from the leaves of the aloe plant, is a popular natural remedy for various skin conditions, thanks to its soothing and healing properties. When applied topically to white scars, aloe vera may offer several potential benefits:
Soothing Effect: Aloe vera gel has a cooling and soothing effect on the skin, which may help alleviate discomfort and irritation associated with white scars.
Hydration and Moisturization: Aloe vera is rich in water content and humectants, making it an effective moisturizer for dry or damaged skin. By keeping the scar tissue hydrated, aloe vera may support the skin’s natural healing process and improve overall skin health.
Scar Healing: While aloe vera is not specifically known for repigmenting scars, its ability to promote wound healing and reduce inflammation may indirectly support melanin production and contribute to scar repigmentation over time.
Onion Extract: Unveiling the Healing Power
Onion extract, derived from the bulbs of the onion plant, has gained popularity in skincare for its potential benefits in scar management and wound healing. When applied topically to white scars, onion extract may offer several advantages:
Scar Reduction: Onion extract contains bioactive compounds such as flavonoids and quercetin, which have been shown to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. By reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, onion extract may help minimize scar tissue and improve skin texture.
Collagen Production: Onion extract is believed to stimulate collagen synthesis in the skin, promoting tissue regeneration and remodeling. By enhancing collagen production, onion extract may contribute to scar repigmentation and overall scar improvement.
Melanogenesis Activation: Some studies suggest that onion extract may stimulate melanin production in the skin, potentially leading to repigmentation of hypopigmented scars. While more research is needed to confirm its efficacy, onion extract remains a promising natural remedy for scar management.
Dietary Changes: Nourishing the Skin from Within
In addition to topical treatments, dietary changes can play a crucial role in supporting skin health and promoting scar repigmentation from within. Incorporating foods rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can provide essential nutrients needed for optimal skin function and healing:
Vitamin C: Found in citrus fruits, berries, and leafy greens, vitamin C is essential for collagen synthesis and wound healing. Including vitamin C-rich foods in your diet can support skin health and promote scar healing.
Vitamin E: Nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils are rich sources of vitamin E, a powerful antioxidant that helps protect the skin from oxidative damage and promote tissue repair. Consuming foods high in vitamin E may support scar repigmentation and overall skin health.
Zinc: Zinc plays a vital role in immune function and wound healing, making it essential for scar management. Foods such as seafood, lean meats, nuts, and whole grains are excellent sources of zinc and can support the skin’s natural healing process.
Limitations of Natural Methods: Setting Realistic Expectations
While natural remedies can offer potential benefits in scar repigmentation, it’s essential to approach them with realistic expectations and an understanding of their limitations:
Variable Results: The effectiveness of natural repigmentation methods may vary depending on individual factors such as scar type, size, location, and skin type. What works for one person may not yield the same results for another.
Time and Patience: Natural repigmentation methods often require time and consistent application to achieve noticeable results. It’s important to be patient and persistent in your efforts, as scar healing and repigmentation are gradual processes that may take weeks to months to see significant improvement.
Incomplete Repigmentation: While natural remedies may help reduce the appearance of white scars, complete repigmentation may not always be achievable. Some scars may retain a lighter pigmentation even with treatment, although they may become less noticeable over time.
Safety Precautions: Prioritizing Skin Health
When exploring natural repigmentation methods for white scars, it’s essential to prioritize skin health and safety:
Patch Testing: Before applying any natural remedy to your scar, conduct a patch test on a small area of skin to check for sensitivity or allergic reactions. Discontinue use if you experience any irritation or discomfort.
Sun Protection: If using sun exposure as a repigmentation method, practice sun safety by wearing sunscreen with a high SPF, seeking shade during peak hours, and wearing protective clothing to minimize the risk of sunburn and skin damage.
Consultation with a Dermatologist: If you have extensive or severe scarring, or if natural remedies fail to produce satisfactory results, consider consulting a dermatologist or qualified healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options. Dermatologists can offer expert guidance and may recommend advanced treatments such as laser therapy or topical medications to address stubborn white scars effectively.
Conclusion: Nurturing Skin Healing Naturally
In the quest to repigment white scars naturally, a holistic approach that combines natural remedies with patience, diligence, and professional guidance is key. By understanding the underlying causes of white scars and harnessing the power of nature through sun exposure, natural oils and butters, aloe vera, onion extract, and dietary changes, individuals can support their skin’s natural healing process and promote scar repigmentation from within. While natural methods may not offer quick or guaranteed results, they can serve as valuable tools in the journey towards healthier, more vibrant skin. Remember, healing takes time, and with patience and persistence, your skin can thrive and shine once again.
[inline_related_posts title=”You Might Be Interested In” title_align=”left” style=”list” number=”6″ align=”none” ids=”6693,6690,6629″ by=”categories” orderby=”rand” order=”DESC” hide_thumb=”no” thumb_right=”no” views=”no” date=”yes” grid_columns=”2″ post_type=”” tax=””]