Paint allergy, though not as widely recognized as some other allergies, can be a significant health concern for individuals who are exposed to paints and related chemicals. Whether you’re a professional painter, a DIY enthusiast, or someone working in an environment where paint is commonly used, understanding how to treat paint allergy is crucial for managing symptoms and preventing long-term health complications. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and most importantly, effective treatment strategies for paint allergy.
Understanding Paint Allergy
Causes of Paint Allergy
Paint allergy occurs when the immune system overreacts to certain chemicals present in paints or their fumes. These chemicals, known as allergens, trigger an immune response in sensitive individuals, leading to various allergic symptoms.
Common Allergens in Paints
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Found in many types of paint, VOCs can cause respiratory irritation and exacerbate allergic reactions.
Formaldehyde: Often present in paint as a preservative, formaldehyde can trigger allergic reactions in susceptible individuals.
Acrylic Compounds: Used in water-based paints, acrylic compounds can cause skin irritation and allergic dermatitis.
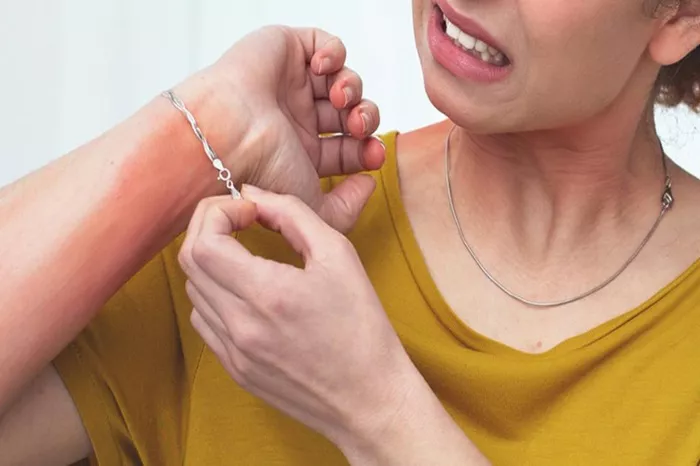
Heavy Metals: Some paints contain heavy metals like chromium and nickel, which can cause allergic reactions upon contact with the skin.
Symptoms of Paint Allergy
The symptoms of paint allergy can vary depending on the individual’s sensitivity and the extent of exposure. Common symptoms include:
Respiratory Issues: Such as coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness.
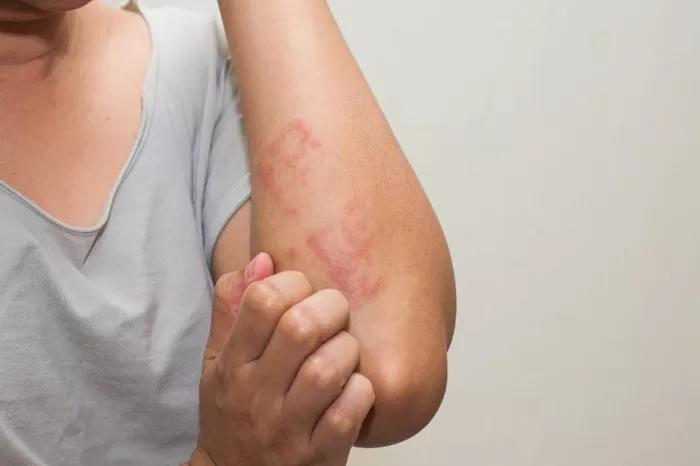
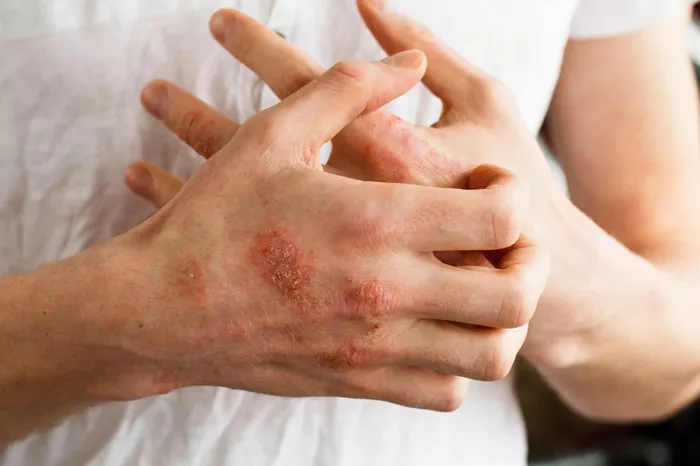
Skin Reactions: Such as itching, redness, swelling, and dermatitis.
Eye Irritation: Including redness, watering, itching, and inflammation.
Nasal Symptoms: Such as sneezing, runny or stuffy nose, and sinus congestion.
Diagnosing Paint Allergy
Medical Evaluation
If you suspect that you have a paint allergy, it’s essential to seek medical evaluation from an allergist or immunologist. They will review your medical history, perform a physical examination, and may conduct various tests to confirm the diagnosis.
Allergy Testing
Skin Prick Test: This test involves placing small amounts of allergens on your skin and then pricking the skin to allow the allergens to enter. If you’re allergic to a particular substance, you’ll likely develop a raised bump or reaction at the test site.
Blood Tests: Blood tests, such as specific IgE tests, can measure the levels of allergy-related antibodies in your blood. Elevated levels of these antibodies can indicate an allergic reaction to specific substances, including paint components.
Environmental Assessment
In addition to medical evaluation and allergy testing, it’s essential to assess your environment for potential sources of paint exposure. Identifying and minimizing exposure to paint allergens is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Treating Paint Allergy
Avoidance of Paint Exposure
The most effective way to manage paint allergy is to avoid exposure to paint and its components as much as possible. This may involve:
Choosing Low-VOC Paints: Opt for paints labeled as low-VOC or VOC-free to reduce exposure to volatile organic compounds.
Proper Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation when painting or working with paints to minimize inhalation of fumes.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wear gloves, goggles, and a mask to protect your skin, eyes, and respiratory system from paint exposure.
Symptomatic Treatment
Respiratory Symptoms
Bronchodilators: For individuals experiencing respiratory issues such as wheezing or shortness of breath, bronchodilators may help relieve symptoms by opening up the airways.
Antihistamines: Antihistamine medications can help alleviate symptoms like sneezing, itching, and nasal congestion by blocking the effects of histamine released during an allergic reaction.
Skin Reactions
Topical Corticosteroids: For allergic dermatitis or skin irritation, topical corticosteroid creams or ointments can help reduce inflammation and itching.
Emollients: Moisturizing creams or emollients can soothe dry, irritated skin and help restore the skin’s natural barrier function.
Eye Irritation
Eye Drops: Lubricating eye drops or artificial tears can provide relief from eye irritation and dryness caused by paint exposure.
Antihistamine Eye Drops: If eye symptoms are due to an allergic reaction, antihistamine eye drops can help alleviate itching and redness.
Allergen Immunotherapy
For individuals with severe or persistent paint allergy symptoms, allergen immunotherapy may be considered. Allergen immunotherapy, also known as allergy shots, involves regular injections of small amounts of the allergen to desensitize the immune system over time.
Conclusion
While paint allergy can be challenging to manage, especially for individuals with frequent exposure to paints and related chemicals, effective treatment strategies are available to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for paint allergy, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize exposure, seek appropriate medical care, and achieve better control of their allergic symptoms. If you suspect that you have a paint allergy, consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and personalized treatment recommendations.
[inline_related_posts title=”You Might Be Interested In” title_align=”left” style=”list” number=”6″ align=”none” ids=”6044,6023,6034″ by=”categories” orderby=”rand” order=”DESC” hide_thumb=”no” thumb_right=”no” views=”no” date=”yes” grid_columns=”2″ post_type=”” tax=””]