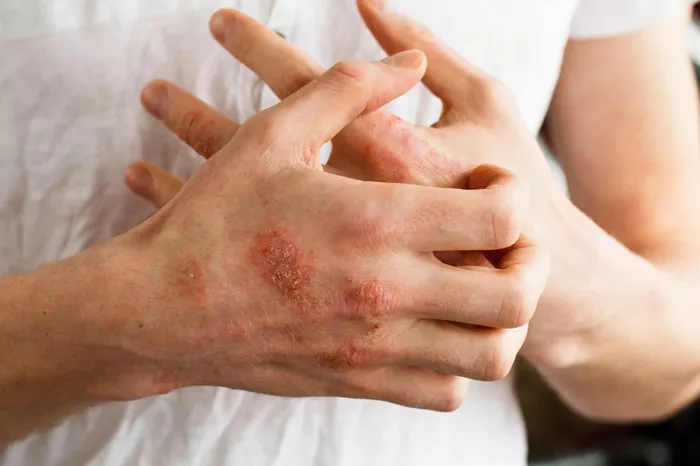
In recent years, hand sanitizers have become ubiquitous in our daily lives, especially with the heightened awareness of personal hygiene due to global health concerns. While these products are essential for preventing the spread of infections, some individuals may experience allergic reactions to certain ingredients found in hand sanitizers. Allergic reactions can range from mild irritation to severe symptoms requiring medical attention. In this guide, we will explore the causes of allergic reactions to hand sanitizers and provide comprehensive strategies for treatment and prevention.
Understanding Allergic Reactions to Hand Sanitizer
Allergic reactions to hand sanitizer typically occur due to sensitivity or allergy to one or more of the ingredients contained in the product. Common ingredients in hand sanitizers that may trigger allergic reactions include:
Alcohol: Most hand sanitizers contain alcohol, such as ethanol or isopropyl alcohol, as the active ingredient. While alcohol is effective at killing germs, it can also cause skin irritation and dryness, particularly in individuals with sensitive skin.
Fragrances: Many hand sanitizers contain added fragrances to improve their scent. These fragrances are composed of various chemicals that can trigger allergic reactions in some people, leading to symptoms such as itching, redness, or rash.
Preservatives: Certain preservatives, such as methylisothiazolinone (MI) or methylchloroisothiazolinone (MCI), are commonly used in hand sanitizers to prevent microbial growth. However, these preservatives have been known to cause allergic contact dermatitis in susceptible individuals.
Other Ingredients: Hand sanitizers may also contain emollients, moisturizers, or other additives to improve their texture and effectiveness. While these ingredients are generally considered safe, they can still cause allergic reactions in some individuals.
Recognizing Symptoms of Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions to hand sanitizer can manifest in various ways, depending on the severity of the allergy and individual sensitivity. Common symptoms of allergic reactions to hand sanitizer include:
Skin Irritation: Redness, itching, burning sensation, or rash on the hands or other exposed areas.
Dryness: Excessive dryness or flakiness of the skin, especially after repeated use of hand sanitizer.
Swelling: Swelling of the hands, fingers, or other affected areas.
Blisters: Formation of blisters or hives on the skin.
Pain or Discomfort: Discomfort or pain upon application of hand sanitizer.
Respiratory Symptoms: In rare cases, inhalation of hand sanitizer fumes may trigger respiratory symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, or shortness of breath.
It is essential to recognize these symptoms promptly and discontinue the use of hand sanitizer if an allergic reaction occurs. Continued use of the product can exacerbate the symptoms and lead to further complications.
Treatment Options for Allergic Reactions
If you experience an allergic reaction to hand sanitizer, several treatment options can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice, especially if the reaction is severe or persists despite home remedies. Below are some common treatment strategies for allergic reactions to hand sanitizer:
[inline_related_posts title=”You Might Be Interested In” title_align=”left” style=”list” number=”6″ align=”none” ids=”6019,6026,6019″ by=”categories” orderby=”rand” order=”DESC” hide_thumb=”no” thumb_right=”no” views=”no” date=”yes” grid_columns=”2″ post_type=”” tax=””]