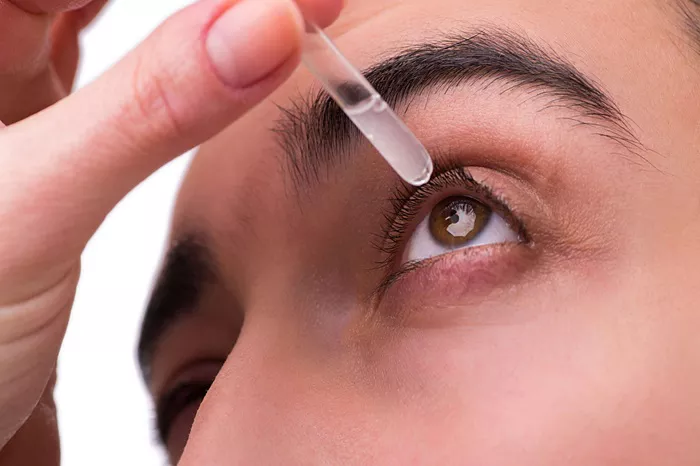
Dry eyes are a common and often uncomfortable symptom experienced by many individuals, especially during allergy seasons. Allergies trigger an inflammatory response in the body, which can lead to various symptoms, including dryness and irritation in the eyes. While managing allergies themselves is essential, addressing dry eyes caused by allergies requires specific approaches. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and most importantly, effective treatment strategies for alleviating dry eyes associated with allergies.
Understanding the Causes and Symptoms
Before delving into treatment options, it’s crucial to understand the underlying causes and symptoms of dry eyes resulting from allergies.
Causes:
Allergic Conjunctivitis: Allergens such as pollen, pet dander, dust mites, and mold spores can trigger allergic reactions in the eyes, leading to inflammation and dryness.
Histamine Release: Allergens prompt the release of histamine in the body, causing blood vessels to dilate and leading to irritation and dryness in the eyes.
Reduced Tear Production: Allergic reactions can interfere with the production of tears, leading to insufficient lubrication and dry eye symptoms.
Symptoms:
Dryness and Grittiness: Individuals may experience a sensation of dryness, grittiness, or a feeling of something foreign in the eyes.
Redness and Irritation: Allergic reactions can cause the eyes to become red, swollen, and irritated.
Excessive Tearing: Paradoxically, dry eyes caused by allergies may also result in excessive tearing as the eyes attempt to compensate for the lack of moisture.
Sensitivity to Light: Some individuals may experience increased sensitivity to light (photophobia) due to dry eyes.
Treatment Strategies
Effective management of dry eyes caused by allergies involves a multifaceted approach, combining environmental modifications, lifestyle changes, and medical interventions. Here are some proven strategies for treating this condition:
1. Allergen Avozidance:
Identify and minimize exposure to allergens triggering allergic reactions. This may involve keeping windows closed during high pollen seasons, using air purifiers, and regularly cleaning surfaces to reduce dust and pet dander.
Practice good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently, especially after outdoor activities, to minimize allergen transfer to the eyes.
2. Lubricating Eye Drops:
Over-the-counter artificial tear drops can provide temporary relief by lubricating the eyes and alleviating dryness and irritation.
Look for preservative-free formulations, as preservatives may exacerbate irritation in some individuals.
Use lubricating eye drops as needed throughout the day, especially in environments with low humidity or high allergen exposure.
3. Cold Compresses:
Applying a cold compress over closed eyelids can help soothe inflammation and reduce swelling and redness associated with allergic reactions.
Use a clean cloth soaked in cold water or a commercially available cold eye mask for 10-15 minutes several times a day as needed.
4. Prescription Medications:
For persistent or severe allergic conjunctivitis, prescription medications may be necessary. Antihistamine eye drops can help block the action of histamine, reducing inflammation and symptoms.
Mast cell stabilizers are another class of medications that prevent the release of histamine, offering long-term relief from allergic reactions in the eyes.
In severe cases, corticosteroid eye drops may be prescribed for short-term use to rapidly reduce inflammation, but long-term use should be avoided due to potential side effects.
5. Immunotherapy:
Immunotherapy, commonly known as allergy shots, can help desensitize the body to specific allergens over time, reducing the severity of allergic reactions.
Allergy shots are administered by a healthcare professional and involve gradually increasing doses of allergens to build tolerance.
While not specifically targeting dry eyes, immunotherapy can indirectly alleviate symptoms by reducing overall allergic response.
6. Dietary Supplements:
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil supplements, have anti-inflammatory properties and may help improve tear production and alleviate dry eye symptoms.
Vitamin D supplements have also been linked to improved eye health and reduced inflammation in some studies.
7. Eyelid Hygiene:
Practicing good eyelid hygiene can help reduce inflammation and blockage of the meibomian glands, which produce the oily component of tears.
Use a warm compress over closed eyelids for 5-10 minutes followed by gentle eyelid massage to promote the secretion of oils and improve tear quality.
Consider using eyelid wipes or baby shampoo diluted in water to clean the eyelids and remove debris or crusts, especially upon waking up in the morning.
8. Humidification:
Using a humidifier in indoor environments can help maintain optimal humidity levels, preventing evaporation of tears and reducing dryness in the eyes.
Ensure proper maintenance of the humidifier to prevent the growth of mold or bacteria, which can exacerbate allergy symptoms.
9. Protective Eyewear:
When outdoors, wearing wrap-around sunglasses can help protect the eyes from allergens such as pollen and reduce irritation and dryness.
Choose sunglasses with 100% UV protection to shield the eyes from harmful ultraviolet rays, which can worsen dry eye symptoms.
Conclusion
Dry eyes resulting from allergies can significantly impact quality of life, causing discomfort and affecting vision. By understanding the underlying causes and implementing appropriate treatment strategies, individuals can effectively manage and alleviate symptoms. From allergen avoidance and lubricating eye drops to prescription medications and immunotherapy, various options are available to address dry eyes caused by allergies. Consulting with an eye care professional is essential for personalized treatment recommendations and optimal management of this condition. With proper care and management, individuals can experience relief from dry eyes and enjoy clear, comfortable vision even during allergy seasons.
[inline_related_posts title=”You Might Be Interested In” title_align=”left” style=”list” number=”6″ align=”none” ids=”6005,6000,6002″ by=”categories” orderby=”rand” order=”DESC” hide_thumb=”no” thumb_right=”no” views=”no” date=”yes” grid_columns=”2″ post_type=”” tax=””]