Strawberries, with their vibrant hue and succulent taste, are a beloved fruit enjoyed by many around the world. However, for some individuals, consuming strawberries can lead to adverse reactions, ranging from mild discomfort to severe allergic responses. In recent years, the prevalence of food allergies, including strawberry allergies, has been on the rise, prompting researchers and medical professionals to delve deeper into understanding the underlying causes. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the intricacies of strawberry allergies, including their potential triggers, symptoms, diagnosis, and management strategies.
1. Strawberry Allergies
Before delving into the specifics of what causes strawberry allergies, it is essential to understand the nature of allergies themselves. Allergies are hypersensitive immune responses triggered by exposure to certain substances known as allergens. In the case of strawberry allergies, the immune system mistakenly identifies proteins present in strawberries as harmful invaders, leading to an immune reaction.
2. The Role of Allergens in Strawberries
Several proteins found in strawberries have been identified as potential allergens. One of the primary allergens in strawberries is Fra a 1, a protein belonging to the pathogenesis-related protein family. Additionally, other proteins, such as Fra a 2 and Fra a 3, have also been implicated in strawberry allergies. These proteins can trigger immune responses in susceptible individuals, leading to allergic reactions.
3. Cross-Reactivity with Pollen Allergens
Cross-reactivity, a phenomenon where the immune system reacts to similar proteins found in different substances, is a common feature of many food allergies, including strawberry allergies. Individuals who are allergic to certain pollens, such as birch pollen or grass pollen, may experience allergic reactions when consuming strawberries due to the presence of proteins that are structurally similar to those found in pollen. This cross-reactivity underscores the complex interplay between environmental allergens and food allergies.
4. Genetic Predisposition to Strawberry Allergies
Genetics play a significant role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to developing allergies, including strawberry allergies. Studies have identified specific genetic markers associated with an increased risk of allergic conditions. Individuals with a family history of allergies are more likely to develop allergic reactions to strawberries and other foods. Understanding the genetic predisposition to strawberry allergies can aid in early detection and personalized management approaches.
5. Environmental Factors and Sensitization
Environmental factors, such as exposure to allergens during infancy and early childhood, play a crucial role in the development of allergic sensitization. Infants who are introduced to strawberries and other potential allergenic foods during the early stages of life may develop tolerance, while delayed introduction or excessive exposure to allergens may increase the risk of allergic reactions. Additionally, environmental factors such as pollution and climate change may influence the prevalence and severity of strawberry allergies.
6. Immunological Mechanisms of Strawberry Allergies
The immune response triggered by strawberry allergens involves complex interactions between various immune cells and molecules. Upon exposure to strawberry proteins, the immune system produces specific antibodies, such as immunoglobulin E (IgE), which recognize and bind to the allergens. This binding triggers the release of inflammatory mediators, such as histamine, leading to the characteristic symptoms of allergic reactions, including itching, swelling, hives, and respiratory symptoms.
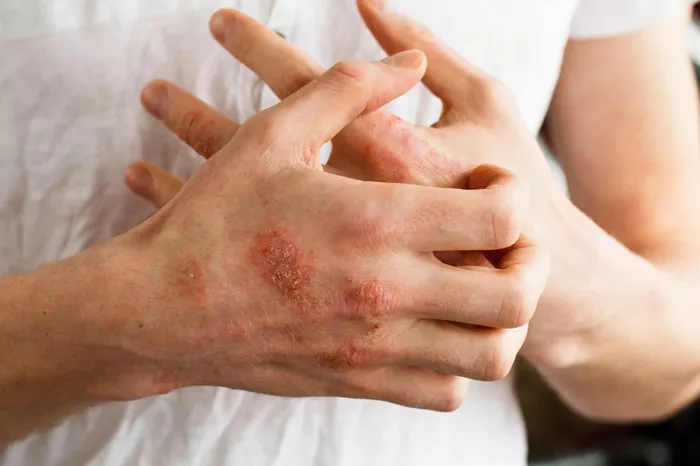
7. Symptoms of Strawberry Allergies
Strawberry allergies can manifest with a wide range of symptoms, varying from mild to severe. Common symptoms of strawberry allergies include:
Skin reactions: Itchy skin, hives (urticaria), redness, and swelling.
Gastrointestinal symptoms: Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.
Respiratory symptoms: Runny nose, sneezing, nasal congestion, coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
Anaphylaxis: A severe, life-threatening allergic reaction characterized by swelling of the throat, difficulty breathing, rapid pulse, and loss of consciousness. Anaphylaxis requires immediate medical attention and administration of epinephrine.
It is important to note that the severity and presentation of symptoms can vary widely among individuals, and allergic reactions may occur shortly after consuming strawberries or be delayed by several hours.
8. Diagnosis of Strawberry Allergies
Accurate diagnosis of strawberry allergies relies on a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Allergy testing, including skin prick tests and blood tests (specific IgE antibodies), can help identify sensitization to strawberry allergens. Additionally, oral food challenges conducted under medical supervision may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and determine the threshold for allergic reactions.
9. Management and Treatment Strategies
Managing strawberry allergies involves avoiding exposure to strawberries and other foods containing strawberry derivatives. Individuals diagnosed with strawberry allergies should carefully read food labels and avoid products that may contain hidden sources of strawberries, such as flavored yogurts, jams, and sauces. In cases of accidental exposure or mild allergic reactions, over-the-counter antihistamines may help alleviate symptoms.
For individuals with a history of severe allergic reactions or anaphylaxis, carrying an epinephrine auto-injector (e.g., EpiPen) at all times is essential. Prompt administration of epinephrine can reverse the symptoms of anaphylaxis and prevent life-threatening complications. It is imperative for individuals with strawberry allergies to develop a personalized allergy action plan in consultation with their healthcare provider.
10. Conclusion
In conclusion, strawberry allergies represent a complex immunological condition characterized by adverse reactions to proteins present in strawberries. Genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and immunological mechanisms contribute to the development and expression of strawberry allergies. Accurate diagnosis, personalized management strategies, and ongoing research efforts are crucial for effectively managing strawberry allergies and improving the quality of life for affected individuals. By gaining a deeper understanding of the underlying causes and mechanisms of strawberry allergies, we can work towards developing more targeted therapies and preventive measures to address this growing public health concern.
[inline_related_posts title=”You Might Be Interested In” title_align=”left” style=”list” number=”6″ align=”none” ids=”5979,5977,5973″ by=”categories” orderby=”rand” order=”DESC” hide_thumb=”no” thumb_right=”no” views=”no” date=”yes” grid_columns=”2″ post_type=”” tax=””]