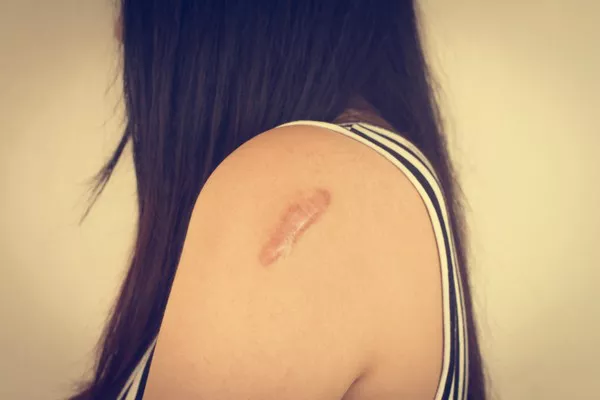
Keloids are a type of raised scar that can develop after an injury, surgery, or even from acne. They are characterized by an overgrowth of collagen fibers in the skin, extending beyond the boundaries of the original wound. Keloids can be aesthetically displeasing and may cause discomfort or itching. Many individuals seek treatment to reduce the appearance and symptoms of keloids. In this article, we will explore the healing process of keloids and discuss factors that can influence the time it takes for them to heal.
Understanding the Keloid Healing Process
Keloids develop as a result of an abnormal response to wound healing. When the skin is injured, the body produces excess collagen, leading to the formation of a raised scar. Unlike normal scars, which tend to fade over time, keloids may continue to grow, becoming larger and more prominent.
The healing process of keloids can be divided into several stages:
Inflammatory Phase: Immediately after the injury or trauma, the body initiates an inflammatory response. Blood vessels dilate, allowing immune cells to migrate to the site of injury. In the case of keloids, this phase may be prolonged and result in excessive collagen production.
Proliferative Phase: During this phase, fibroblasts, specialized cells responsible for producing collagen, migrate to the wound site and begin synthesizing new collagen fibers. In keloids, this process is often disrupted, leading to an overproduction of collagen.
Maturation Phase: In normal wound healing, the excess collagen fibers are gradually broken down and remodeled, resulting in a flatter and less noticeable scar. However, in keloids, this phase may be delayed or incomplete, leading to the persistence of raised scar tissue.
Factors Influencing Keloid Healing Time
The time it takes for a keloid to heal can vary significantly depending on various factors. Here are some key factors that can influence the healing process:
Size and Severity: Larger keloids or those that extend deeper into the skin may take longer to heal compared to smaller, less severe keloids. The size and severity of the keloid can impact the time it takes for the excess collagen to break down and the scar to flatten.
Location: The location of the keloid can affect the healing time. Keloids in areas with more blood supply, such as the chest or earlobes, may heal faster than those in areas with poorer blood circulation, like the shoulders or back.
Individual Healing Factors: Each person’s healing process is unique. Factors such as age, overall health, and immune function can influence how quickly the body repairs and remodels the keloid. Younger individuals tend to heal faster than older individuals, and those with compromised immune systems may experience delayed healing.
Treatment Interventions: The type of treatment received for keloids can impact the healing time. Various treatment options, including corticosteroid injections, silicone gel sheets, cryotherapy, laser therapy, and surgical excision, may be used to manage keloids. The specific treatment modality and its effectiveness can influence the healing process.
Average Healing Time for Keloids
It is important to note that the healing time for keloids can vary significantly from person to person. While some keloids may show improvement over a few months, others may take several years to heal. In general, the healing process for keloids is often slow, and complete resolution may not be achievable in all cases.
It is common for keloids to gradually improve over time, becoming less raised, softer, and lighter in color. However, complete elimination of a keloid is challenging, and recurrence may occur even after successful treatment.
Patient Expectations and Care
Managing patient expectations is crucial when it comes to keloid healing. Patients should understand that the healing process for keloids is often prolonged, and complete resolution may not be attainable. Instead, the goal of treatment is typically to reduce the size, symptoms, and cosmetic appearance of the keloid.
In addition to treatment interventions, proper wound care and maintenance can aid in the healing process. This may include keeping the area clean, avoiding excessive tension or trauma to the keloid, and using appropriate scar management techniques, such as silicone gel sheets or ointments.
Conclusion
The healing time for keloids is highly variable and can be influenced by factors such as size, severity, location, individual healing factors, and treatment interventions. While keloids often heal slowly and may not completely resolve, various treatment options are available to manage their appearance and symptoms. It is essential for patients to have realistic expectations and work closely with a dermatologist or healthcare professional to develop an individualized treatment plan. Through proper care and treatment, the healing process of keloids can be optimized, leading to improved outcomes and patient satisfaction.
[inline_related_posts title=”Related Topics” title_align=”left” style=”list” number=”3″ align=”none” ids=”460,447,457″ by=”categories” orderby=”rand” order=”DESC” hide_thumb=”no” thumb_right=”no” views=”no” date=”yes” grid_columns=”1″ post_type=”” tax=””]