Scars, whether from injuries, surgeries, or skin conditions, often prompt the question: How long does it take for small scars to fade? The journey from a fresh wound to a faded scar is a complex process influenced by various factors. This article delves into the intricacies of scar healing, exploring the timelines and variables that contribute to the gradual fading of small scars.
The Initial Healing Phase
In the initial days and weeks after a wound has closed, the focus is on the body’s natural healing processes. During this time, the formation of a scar begins. The first step involves inflammation, where the body works to clean and repair the wound. The initial healing phase sets the stage for the subsequent events that will dictate how long it will take for small scars to fade.
Types of Scars
The type of scar plays a pivotal role in determining how long it takes for it to fade. There are various types of scars, including hypertrophic scars, keloid scars, and atrophic scars, each with its own distinct characteristics. Hypertrophic and keloid scars, characterized by raised and thickened tissue, may take longer to fade compared to atrophic scars, which result in a depression in the skin. Understanding the specific type of scar can provide insights into the anticipated timeline for fading.
Wound Care Practices
Proper wound care in the early stages of healing can significantly impact the subsequent scar fading process. Keeping the wound clean, moisturized, and protected from infection is crucial. The use of topical treatments, such as silicone sheets or gels, can also influence scar formation and, consequently, how long it takes for small scars to fade. Consistent and appropriate wound care practices create an optimal environment for the skin’s natural healing mechanisms.
Genetic Factors
Genetic factors contribute to the variability in how long it takes for small scars to fade. The propensity to develop certain types of scars, the efficiency of the body’s healing mechanisms, and the overall skin structure are influenced by genetics. Individuals with a family history of slow or rapid scar fading may experience similar patterns. While genetics lay the foundation, lifestyle and environmental factors also play crucial roles in shaping the scar fading process.
Skin Type and Color
Skin type and color influence how scars appear and how quickly they fade. In individuals with lighter skin tones, scars may be more noticeable initially but tend to fade over time. On the other hand, darker skin tones may experience hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation in scars, impacting their appearance and the time it takes for them to fade. Understanding the diversity in skin types and colors allows for a more nuanced assessment of scar fading timelines.
Age as a Factor
Age is another factor that contributes to the variability in scar fading timelines. Younger individuals tend to have more robust healing processes, often resulting in faster scar fading. The skin’s regenerative capacity is typically higher in youth. However, older individuals may experience slower scar fading due to the natural aging processes that affect skin elasticity and collagen production. Acknowledging the role of age provides context to the expected duration of scar fading.
Sun Exposure
Sun exposure can either aid or hinder the scar fading process. While some sun exposure is beneficial for the skin’s overall health, excessive sun exposure can have detrimental effects on scars. UV rays can cause hyperpigmentation, making scars more noticeable and prolonging the time it takes for small scars to fade. Sun protection measures, such as sunscreen application and avoiding direct sunlight, are essential considerations in managing scar fading.
Scar Massage and Physical Therapy:
Scar massage and physical therapy are proactive approaches that can accelerate the scar fading process. Gently massaging the scar tissue helps break down collagen fibers and align them in a more organized fashion. Physical therapy techniques, such as stretching and mobilization, contribute to improved tissue flexibility. Integrating these practices into the scar management plan can positively influence how long it takes for small scars to fade.
Over-the-Counter Products
The market offers a myriad of over-the-counter products specifically designed to promote scar fading. These may include creams, gels, or silicone-based sheets that claim to improve the appearance of scars. While some individuals may find these products beneficial, their efficacy can vary. It’s essential to choose products with evidence-based ingredients and to manage expectations regarding the gradual nature of scar fading.
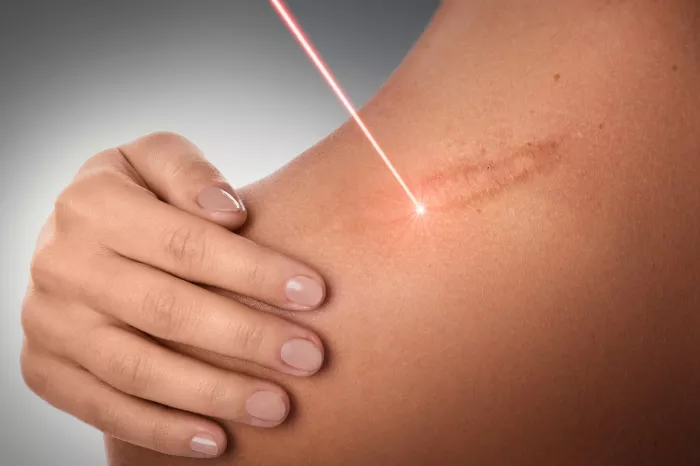
Professional Interventions
For individuals seeking more aggressive or targeted approaches, professional interventions are available. Dermatologists and plastic surgeons can provide treatments such as laser therapy, microdermabrasion, or corticosteroid injections to address scars. These interventions are tailored to individual needs and can be instrumental in optimizing scar fading timelines. Consulting with a healthcare professional ensures a personalized and effective approach to scar management.
Conclusion
The journey from a fresh wound to a faded scar is a nuanced process influenced by a multitude of factors. As individuals ponder how long it takes for small scars to fade, it’s crucial to recognize the dynamic interplay of genetics, wound care practices, lifestyle choices, and environmental influences. Embracing the gradual nature of scar fading allows individuals to make informed decisions, implementing strategies that align with their unique circumstances. Whether through diligent wound care, lifestyle modifications, or professional interventions, the path to scar fading is a journey that unfolds over time, with patience and proactive choices guiding the way.
[inline_related_posts title=”You Might Be Interested In” title_align=”left” style=”list” number=”6″ align=”none” ids=”3331,3329,3327″ by=”categories” orderby=”rand” order=”DESC” hide_thumb=”no” thumb_right=”no” views=”no” date=”yes” grid_columns=”2″ post_type=”” tax=””]