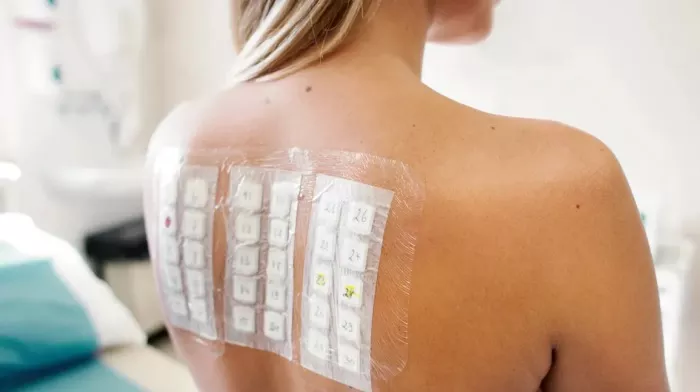
In the realm of allergic reactions and dermatological conditions, the allergy patch test stands as a crucial diagnostic tool. This specialized examination method plays a pivotal role in identifying the allergens responsible for a wide array of skin-related issues. With the prevalence of allergies on the rise, understanding the intricacies of the allergy patch test is more important than ever. In this comprehensive article, we will delve deep into what an allergy patch test is, how it works, its significance in modern medicine, and what you can expect if you undergo one.
The Genesis of Allergies and the Need for Allergy Patch Tests
Before we dive into the specifics of the allergy patch test, it’s essential to comprehend the fundamentals of allergies. An allergy is essentially an exaggerated immune response to a foreign substance, known as an allergen. Allergies can manifest in various ways, including respiratory symptoms, gastrointestinal distress, and skin reactions. When it comes to skin-related allergic reactions, the allergy patch test becomes a critical tool in identifying the causative allergens.
What is an Allergy Patch Test?
So, what exactly is an allergy patch test? In essence, it is a diagnostic procedure used by dermatologists and allergists to identify allergens that may be triggering skin conditions. This test involves the application of allergen-containing patches to a patient’s skin. The patches are left in place for a specified period, typically 48 hours, during which the skin’s reaction to the allergens is closely monitored. By observing the skin’s response, healthcare professionals can pinpoint the specific allergens responsible for a patient’s allergic contact dermatitis or other skin-related allergic reactions.
The Mechanics of an Allergy Patch Test
The mechanics of an allergy patch test may seem straightforward, but they are intricately designed to provide precise results. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how this diagnostic procedure is carried out:
Consultation and Assessment: The process begins with a thorough consultation between the patient and the healthcare provider. During this consultation, the patient’s medical history is reviewed, and any pertinent information regarding the suspected allergens is gathered.
Patch Selection: Based on the information obtained, the healthcare provider selects a series of allergen patches that are relevant to the patient’s condition. These patches contain small amounts of common allergens, such as nickel, fragrances, or preservatives.
Application of Allergen Patches: The selected allergen patches are then applied to the patient’s back, typically in an organized grid pattern. Each patch is secured with hypoallergenic adhesive tape.
Waiting Period: The patient is instructed to keep the patches on their skin for a specific duration, usually 48 hours. During this time, it’s essential to avoid activities that could disrupt the patches or lead to excessive sweating.
Evaluation: After the waiting period, the patient returns to the healthcare provider’s office for an evaluation. The healthcare provider carefully examines the skin under each patch to look for any signs of an allergic reaction.
Interpretation: The results are typically graded on a scale from negative to strongly positive, depending on the severity of the skin reaction. This grading helps determine the degree of sensitivity to each tested allergen.
Discussion and Planning: Based on the results of the allergy patch test, the healthcare provider discusses the findings with the patient. Together, they develop a plan for managing and avoiding exposure to the identified allergens.
Significance of Allergy Patch Tests
Now that we have a clear understanding of what an allergy patch test entails, let’s explore why this diagnostic procedure is so significant in the field of dermatology and allergy management.
Accurate Identification of Allergens: One of the primary benefits of an allergy patch test is its ability to accurately identify the specific allergens causing a patient’s skin reactions. This precision allows for targeted treatment and avoidance strategies.
Customized Treatment Plans: Armed with the knowledge of which allergens are triggering a patient’s symptoms, healthcare providers can create customized treatment plans. This might include recommending allergen avoidance, prescribing topical corticosteroids, or providing other appropriate interventions.
Preventing Recurrence: By identifying and addressing the root causes of allergic reactions, allergy patch tests play a crucial role in preventing recurrence. Patients can take proactive measures to minimize exposure to the identified allergens.
Research and Product Development: Allergy patch test results contribute to ongoing research in the field of dermatology and allergology. They help scientists and clinicians better understand the prevalence of various allergens and their impact on the population.
Common Skin Conditions Diagnosed Using Allergy Patch Tests
The utility of allergy patch tests extends to a wide range of skin conditions. Let’s take a closer look at some of the common dermatological issues diagnosed using this diagnostic method:
Allergic Contact Dermatitis: Allergic contact dermatitis is a skin condition characterized by redness, itching, and rash in response to contact with allergenic substances. An allergy patch test is often used to identify the specific allergen responsible for this condition, which can include substances like fragrances, preservatives, or metals like nickel.
Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema): While eczema is often associated with genetic factors, allergens can exacerbate symptoms. An allergy patch test can help determine if certain allergens are contributing to a patient’s eczema flare-ups.
Occupational Skin Conditions: Individuals in certain professions may be exposed to occupational allergens, such as chemicals or plants. An allergy patch test can be instrumental in identifying and managing these workplace-related skin issues.
Cosmetic Allergies: Some individuals may experience adverse skin reactions to cosmetics and skincare products. An allergy patch test can pinpoint the specific ingredient causing the allergic reaction, allowing the patient to select hypoallergenic alternatives.
Medication Allergies: In cases of suspected medication allergies with skin manifestations, an allergy patch test can help confirm the allergen responsible. This information is crucial for avoiding the allergenic medication in the future.
Preparing for an Allergy Patch Test
If you are scheduled for an allergy patch test, there are some essential steps you should take to ensure accurate results and a smooth testing process. Here’s a checklist to help you prepare:
Medication Review: Inform your healthcare provider about any medications you are currently taking, as some drugs may interfere with the test results.
Skin Preparation: Ensure your back is clean and free from any lotions, creams, or ointments on the day of the test. Avoid shaving the area to be tested.
Avoiding Sun Exposure: It’s advisable to avoid prolonged sun exposure to the test area for at least a week before the test. Sunburn or tanning can affect the test results.
Patch Duration: Be prepared to keep the patches on your back for the specified duration, usually 48 hours. During this time, try to avoid activities that may cause excessive sweating or friction on the patch area.
Follow Instructions: Carefully follow any pre-test instructions provided by your healthcare provider, such as dietary restrictions or other specific guidelines.
Post-Test Care: After the patches are removed and the healthcare provider evaluates the results, follow any post-test care instructions, which may include applying soothing creams or ointments if necessary.
Interpreting Allergy Patch Test Results
Understanding the results of an allergy patch test requires some knowledge of how the test is interpreted. The following is a general guide to help you make sense of the results:
Negative Reaction: A negative reaction means there was no significant skin response to the tested allergen. This suggests that you are unlikely to be allergic to that particular substance.
Weak Positive Reaction: A weak positive reaction typically indicates mild sensitivity to the tested allergen. While it may not cause severe symptoms, it’s still essential to be aware of this sensitivity and take precautions to avoid the allergen.
Strong Positive Reaction: A strong positive reaction suggests a significant sensitivity or allergy to the tested allergen. This allergen is likely responsible for your skin symptoms, and you should take measures to avoid exposure.
Irritant Reaction: Sometimes, an irritant reaction may occur, which is not an allergic response but rather a response to the irritative properties of the substance. Your healthcare provider will differentiate between irritant and allergic reactions.
Allergy Patch Tests: Beyond the Basics
While we’ve covered the fundamental aspects of allergy patch tests, there are several advanced and specialized variations of this diagnostic procedure. These include:
Extended Patch Testing: In cases where standard patch tests do not yield conclusive results, extended patch testing may be performed. This involves an extended panel of allergens to identify less common sensitivities.
Photo-Patch Testing: Photo-patch testing combines patch testing with exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light. It is used to diagnose photo-allergic reactions, where allergens become reactive when exposed to sunlight.
Patch Testing for Children: Allergy patch tests can be modified for use in pediatric patients to identify allergens causing skin issues in children. The procedure is typically adapted to suit the child’s age and condition.
Metal Allergy Testing: Metal allergens, such as nickel, cobalt, and chromium, are common culprits in allergic contact dermatitis. Specialized metal allergy patch tests can help identify these sensitivities.
Potential Challenges and Limitations of Allergy Patch Tests
While allergy patch tests are invaluable diagnostic tools, they are not without their limitations and challenges. It’s crucial to be aware of these factors:
Delayed Results: Unlike some allergy tests that provide immediate results, patch tests require patience. Results are typically evaluated after the patches are removed, which can take 48 hours or longer.
False Positives: In some cases, a positive reaction may occur even if the allergen is not responsible for the patient’s symptoms. This is why the test should be interpreted by a trained healthcare provider with expertise in dermatology and allergy.
Irritant Reactions: As mentioned earlier, irritant reactions can mimic allergic responses. Distinguishing between the two is a key challenge in interpreting patch test results accurately.
Limited Scope: Patch tests can only identify contact allergens, meaning allergens that come into direct contact with the skin. They do not detect allergens that trigger systemic (body-wide) allergic reactions, such as those causing food allergies or hay fever.
Skin Condition Variability: Skin conditions can change over time, and the results of an allergy patch test may not remain constant throughout a person’s life. Repeated testing may be necessary in some cases.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of allergies and dermatological conditions, the allergy patch test remains a stalwart diagnostic tool. Its ability to pinpoint specific allergens responsible for skin reactions has transformed the way healthcare providers approach diagnosis and treatment. Armed with the knowledge of allergenic triggers, patients can take proactive steps to manage their conditions and improve their quality of life. While the allergy patch test may have its challenges and limitations, its significance in the field of dermatology and allergology cannot be overstated. As allergies continue to affect millions of individuals worldwide, the allergy patch test remains an essential ally in the quest for accurate diagnosis and effective management.
[inline_related_posts title=”You Might Be Interested In” title_align=”left” style=”list” number=”6″ align=”none” ids=”2710,2703,2699″ by=”categories” orderby=”rand” order=”DESC” hide_thumb=”no” thumb_right=”no” views=”no” date=”yes” grid_columns=”2″ post_type=”” tax=””]