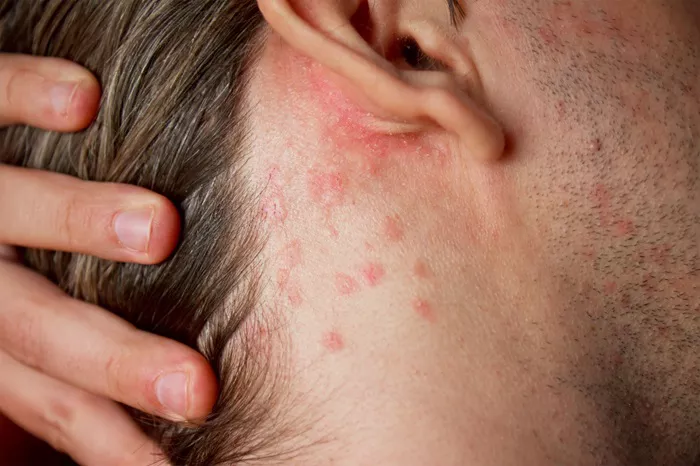
Mold allergies are a common issue that many people face, leading to a range of symptoms that can significantly impact daily life. Understanding how long these symptoms last after exposure is crucial for managing and mitigating their effects. This article delves into the duration of mold allergy symptoms, factors influencing their persistence, and strategies for relief and prevention.
Understanding Mold Allergies
What Are Mold Allergies?
Mold allergies occur when the immune system overreacts to mold spores, treating them as harmful invaders. Molds are fungi that thrive in damp, warm, and humid environments. When mold spores are inhaled or come into contact with the skin, they can trigger allergic reactions in susceptible individuals.
Common Mold Types
Several types of mold can cause allergic reactions, including:
Cladosporium: Often found indoors and outdoors, it can grow on textiles, wood, and other damp surfaces.
Penicillium: Commonly found on decaying fabrics, wallpaper, and carpet, it can also contaminate food.
Aspergillus: Found in dust, this mold can grow on various surfaces, including walls and insulation.
Alternaria: Typically found outdoors, it can also grow indoors in damp places like showers and under sinks.
Symptoms of Mold Allergies
Mold allergy symptoms can vary from mild to severe and may include:
- Sneezing
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Itchy or watery eyes
- Coughing
- Postnasal drip
- Wheezing
- Skin rash or hives
In individuals with asthma, mold exposure can trigger asthma attacks or worsen existing asthma symptoms.
Duration of Mold Allergy Symptoms
Immediate Symptoms
Mold allergy symptoms can appear immediately upon exposure to mold spores. These acute reactions are often characterized by sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes. The severity and duration of these immediate symptoms can vary based on the level of exposure and individual sensitivity.
Persistent Symptoms
For some individuals, mold allergy symptoms can persist long after the initial exposure. Factors influencing the duration of these symptoms include:
Continued Exposure: Ongoing exposure to mold, even at low levels, can prolong symptoms.
Sensitivity Levels: Individuals with higher sensitivity to mold may experience longer-lasting symptoms.
Environmental Factors: Humidity and ventilation levels in the living environment can affect how long mold spores remain airborne, impacting symptom duration.
Chronic Symptoms
In cases of prolonged or repeated exposure to mold, individuals may develop chronic symptoms. These can include persistent respiratory issues, chronic sinusitis, and skin rashes. Chronic exposure can also lead to more severe health issues, particularly in individuals with compromised immune systems or preexisting respiratory conditions.
Factors Influencing Symptom Duration
Amount of Exposure
The amount of mold exposure plays a significant role in determining how long symptoms last. Higher levels of exposure typically result in more severe and prolonged symptoms. Reducing exposure by eliminating mold sources and improving indoor air quality can help alleviate symptoms more quickly.
Individual Sensitivity
Individual sensitivity to mold varies widely. Some people may experience mild symptoms that resolve quickly, while others may have more severe reactions that persist for longer periods. Factors influencing individual sensitivity include genetic predisposition, existing allergies, and overall health.
Environmental Conditions
Environmental conditions, such as humidity and temperature, can impact the persistence of mold spores in the air and on surfaces. High humidity levels create favorable conditions for mold growth and spore dispersion, prolonging exposure and symptoms. Improving ventilation and using dehumidifiers can help reduce mold growth and alleviate symptoms.
Immune System Response
The strength and response of an individual’s immune system also influence the duration of mold allergy symptoms. A strong immune system may resolve symptoms more quickly, while a compromised immune system may lead to prolonged and more severe reactions. Individuals with preexisting conditions, such as asthma or chronic sinusitis, may experience longer-lasting symptoms.
Managing and Alleviating Mold Allergy Symptoms
Immediate Relief Measures
Antihistamines
Antihistamines are commonly used to alleviate immediate allergy symptoms. They work by blocking histamine, a chemical released by the immune system during an allergic reaction. Over-the-counter antihistamines can help reduce sneezing, itching, and runny nose.
Nasal Corticosteroids
Nasal corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation in the nasal passages, providing relief from congestion and runny nose. These medications are available over-the-counter or by prescription and are effective for managing persistent symptoms.
Decongestants
Decongestants can help relieve nasal congestion by narrowing blood vessels in the nasal passages. They are available in oral or nasal spray forms. However, they should be used with caution, as prolonged use of nasal decongestant sprays can lead to rebound congestion.
See Also: Grass Rash: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Long-Term Management Strategies
Allergen Avoidance
The most effective way to manage mold allergy symptoms is to avoid exposure to mold spores. This involves identifying and eliminating mold sources in the living environment. Key steps include:
Fixing Leaks: Repairing leaks in roofs, walls, and plumbing to prevent mold growth.
Improving Ventilation: Using exhaust fans, dehumidifiers, and air purifiers to reduce humidity and improve air quality.
Regular Cleaning: Cleaning and disinfecting areas prone to mold growth, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and basements.
Removing Mold: Safely removing mold from surfaces using appropriate cleaning agents and protective equipment.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy, also known as allergy shots, involves gradually exposing the individual to small amounts of the allergen to build tolerance over time. This treatment can be effective for individuals with severe or persistent mold allergies. Immunotherapy requires a long-term commitment and should be administered under the supervision of a healthcare professional.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making lifestyle modifications can help reduce the risk of mold exposure and alleviate symptoms. These include:
Using Air Purifiers: Air purifiers with HEPA filters can help remove mold spores from the air.
Maintaining Low Humidity: Keeping indoor humidity levels below 50% to prevent mold growth.
Wearing Protective Gear: Using masks and gloves when cleaning moldy areas to reduce direct exposure.
Regularly Inspecting Homes: Conducting routine inspections for signs of mold growth and addressing issues promptly.
Medical Interventions
Prescription Medications
In cases of severe or persistent mold allergy symptoms, prescription medications may be necessary. These can include stronger antihistamines, corticosteroids, or leukotriene inhibitors. A healthcare professional can assess the severity of the symptoms and recommend appropriate medications.
Sinus Irrigation
Sinus irrigation, also known as nasal lavage or nasal irrigation, involves rinsing the nasal passages with a saline solution. This can help remove allergens and mucus, providing relief from nasal congestion and sinus pressure. Sinus irrigation devices, such as neti pots or squeeze bottles, can be used for this purpose.
Treatment for Asthma
For individuals with asthma, managing mold allergies is crucial to prevent asthma attacks and complications. Inhalers and other asthma medications can help control symptoms and reduce the risk of severe reactions. A comprehensive asthma action plan should be developed in consultation with a healthcare provider.
Preventing Mold Allergies
Home Maintenance and Repair
Regular home maintenance and repair are essential to prevent mold growth and reduce allergy symptoms. Key measures include:
Fixing Leaks Promptly: Addressing leaks in roofs, walls, and plumbing to prevent moisture accumulation.
Improving Drainage: Ensuring proper drainage around the home to prevent water seepage and mold growth.
Cleaning Gutters: Regularly cleaning gutters to prevent water buildup and mold growth.
Controlling Indoor Humidity
Controlling indoor humidity levels is crucial for preventing mold growth. Strategies include:
Using Dehumidifiers: Dehumidifiers can help maintain optimal humidity levels, particularly in damp areas like basements.
Ventilating: Ensuring adequate ventilation in bathrooms, kitchens, and laundry areas to reduce moisture buildup.
Air Conditioning: Using air conditioning to control temperature and humidity during hot and humid weather.
Regular Cleaning and Inspection
Regular cleaning and inspection can help identify and address mold issues before they become severe. Tips include:
Using Mold-Resistant Products: Using mold-resistant paints and building materials in areas prone to moisture.
Inspecting for Mold: Conducting routine inspections for signs of mold growth, particularly in damp areas.
Cleaning with Mold-Killing Products: Using cleaning products specifically designed to kill mold spores and prevent regrowth.
Education and Awareness
Raising awareness about mold allergies and prevention strategies can help individuals take proactive steps to reduce exposure and manage symptoms. Educational resources, support groups, and professional guidance can provide valuable information and support.
Conclusion
Mold allergy symptoms can vary in duration and severity based on factors such as exposure levels, individual sensitivity, and environmental conditions. Immediate relief measures, long-term management strategies, and preventive measures are crucial for effectively managing and alleviating mold allergy symptoms. By understanding the nature of mold allergies and implementing comprehensive strategies, individuals can improve their quality of life and reduce the impact of mold exposure on their health.
[inline_related_posts title=”You Might Be Interested In” title_align=”left” style=”list” number=”6″ align=”none” ids=”10569,10533,10497″ by=”categories” orderby=”rand” order=”DESC” hide_thumb=”no” thumb_right=”no” views=”no” date=”yes” grid_columns=”2″ post_type=”” tax=””]