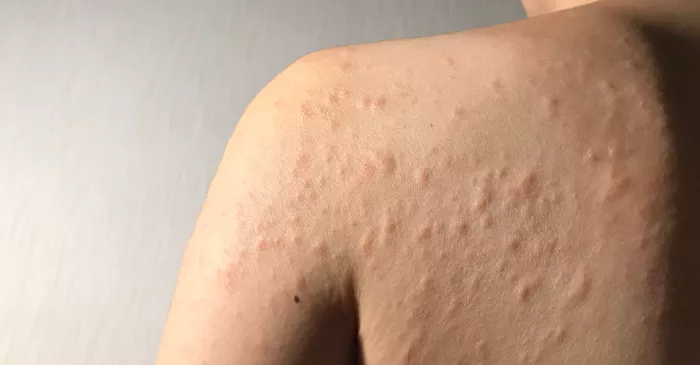
Grass rash is a common skin condition that many people experience, especially during the warmer months when outdoor activities are prevalent. This article delves into the various aspects of grass rash, including its causes, symptoms, preventive measures, and treatment options. By understanding grass rash, individuals can better manage and prevent this irritating condition, ensuring a more comfortable outdoor experience.
What is Grass Rash?
Grass rash, also known as grass allergy rash or contact dermatitis, is a type of skin inflammation that occurs when the skin comes into contact with certain plants or grasses. This condition is characterized by redness, itching, and sometimes blistering of the skin. While it can affect people of all ages, those who spend a lot of time outdoors, such as gardeners, athletes, and children, are more susceptible.
Causes of Grass Rash
The primary cause of grass rash is exposure to allergens present in various types of grasses and plants. When these allergens come into contact with the skin, they can trigger an immune response, leading to the symptoms of grass rash. Here are some common factors that contribute to the development of grass rash:
Allergenic Plants
Certain plants are more likely to cause allergic reactions than others. Some common culprits include:
Poison Ivy, Oak, and Sumac: These plants contain urushiol, a potent allergen that can cause severe rashes.
Bermuda Grass: Widely used in lawns and sports fields, Bermuda grass can cause skin irritation in sensitive individuals.
Ragweed: Known for causing hay fever, ragweed can also cause skin reactions upon contact.
Pollen and Airborne Allergens
Pollen from grasses and other plants can settle on the skin, leading to allergic reactions. During high pollen seasons, individuals may notice an increase in grass rash symptoms.
Mechanical Irritation
The physical action of grass blades rubbing against the skin can cause irritation, especially if the skin is already sensitive or damaged. This mechanical irritation can exacerbate the allergic reaction.
Chemical Irritants
Lawn care products such as fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides can contribute to skin irritation and increase the risk of developing grass rash. These chemicals can either directly irritate the skin or enhance the allergic response to grass allergens.
Symptoms of Grass Rash
The symptoms of grass rash can vary in severity, depending on the individual’s sensitivity and the extent of exposure to the allergens. Common symptoms include:
Redness and Inflammation
One of the most noticeable symptoms of grass rash is redness and swelling of the affected area. The skin may appear flushed and feel warm to the touch.
Itching and Burning Sensation
Itching is a hallmark symptom of grass rash. The affected area may also feel like it is burning, leading to discomfort and the urge to scratch, which can worsen the condition.
Blisters and Hives
In more severe cases, small blisters or hives may develop on the skin. These blisters can be filled with fluid and may burst, leading to further irritation and potential infection.
Dry and Scaly Skin
Prolonged exposure to allergens can cause the skin to become dry and scaly. This can result in peeling and flaking, which can be both unsightly and uncomfortable.
Swelling
Swelling around the affected area is common and can be particularly concerning if it occurs near the eyes, lips, or throat, as it may impede normal functioning and breathing.
Diagnosis of Grass Rash
Proper diagnosis is essential for effective treatment and management of grass rash. A healthcare professional can diagnose the condition through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests.
Medical History and Physical Examination
During the consultation, the healthcare provider will ask about the patient’s medical history, including any known allergies, previous episodes of rashes, and recent outdoor activities. A thorough physical examination of the rash will help in identifying its characteristics and severity.
Patch Testing
Patch testing involves applying small amounts of potential allergens to the skin under adhesive patches. These patches are left in place for 48 hours, and the skin’s reaction is observed. This test can help identify specific allergens responsible for the rash.
Skin Prick Test
In a skin prick test, small amounts of allergens are introduced into the skin through tiny punctures. If the skin reacts with redness and swelling at the test site, it indicates an allergy to that particular substance.
See Also: 12 Best Solutions for Pimple Scars: A Comprehensive Guide
Blood Tests
Blood tests can measure the levels of specific antibodies (IgE) that the body produces in response to allergens. Elevated levels of these antibodies can confirm an allergic reaction.
Preventive Measures for Grass Rash
Preventing grass rash involves minimizing exposure to allergens and taking steps to protect the skin. Here are some effective preventive measures:
Avoidance of Allergenic Plants
Identify and avoid contact with plants known to cause allergic reactions. Learning to recognize plants like poison ivy, oak, and sumac can help reduce the risk of exposure.
Protective Clothing
Wearing long sleeves, pants, and gloves when working or playing in grassy areas can create a physical barrier between the skin and allergens. Additionally, hats and sunglasses can protect the face and eyes.
Showering After Outdoor Activities
Showering immediately after spending time outdoors can help wash off pollen and other allergens from the skin and hair. This reduces the likelihood of prolonged exposure and subsequent reactions.
Using Protective Barriers
Applying barrier creams or lotions designed to protect the skin from allergens can be effective. These products create a protective layer that prevents direct contact with irritants.
Maintaining a Clean Environment
Regularly mowing the lawn and keeping grassy areas well-maintained can reduce the amount of pollen and plant debris. Using air purifiers and keeping windows closed during high pollen seasons can also help.
Treatment Options for Grass Rash
Treating grass rash involves alleviating symptoms and promoting skin healing. Depending on the severity of the rash, different treatment options may be recommended.
Over-the-Counter Treatments
For mild cases of grass rash, over-the-counter treatments can be effective in managing symptoms:
Antihistamines
Oral antihistamines such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or cetirizine (Zyrtec) can help reduce itching and inflammation by blocking histamine, a chemical released during allergic reactions.
Topical Corticosteroids
Hydrocortisone creams and ointments can be applied directly to the rash to reduce inflammation and itching. These are available without a prescription for mild rashes.
Calamine Lotion
Calamine lotion can soothe itching and provide a cooling effect, offering temporary relief from discomfort.
Prescription Medications
In more severe cases, prescription medications may be necessary:
Stronger Corticosteroids
Prescription-strength corticosteroid creams or oral steroids may be prescribed to reduce severe inflammation and itching.
Immunosuppressants
For chronic or severe allergic reactions, immunosuppressant medications may be used to reduce the body’s immune response.
Home Remedies
Several home remedies can provide relief from grass rash symptoms:
Cool Compresses
Applying cool, damp cloths to the affected area can help reduce itching and swelling.
Oatmeal Baths
Soaking in an oatmeal bath can soothe irritated skin and provide relief from itching.
Aloe Vera
Aloe vera gel has anti-inflammatory properties that can help soothe and heal the skin.
Avoiding Irritants
Avoiding further exposure to the irritants that caused the rash is crucial. Identifying and steering clear of the specific grass or plant responsible for the reaction can prevent future episodes.
Complications of Grass Rash
While grass rash is generally a mild condition, complications can arise if it is not properly managed. Here are some potential complications:
Infection
Scratching the rash can break the skin, creating an entry point for bacteria. This can lead to bacterial infections, which may require antibiotic treatment.
Chronic Dermatitis
Repeated exposure to allergens can lead to chronic dermatitis, characterized by persistent itching, redness, and thickened skin.
Allergic Sensitization
Prolonged exposure to allergens can increase the body’s sensitivity, leading to more severe reactions over time.
Impact on Quality of Life
Severe or chronic grass rash can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, causing discomfort, sleep disturbances, and limiting outdoor activities.
Conclusion
Grass rash, while often a mild and manageable condition, can cause significant discomfort and inconvenience. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for effective management and prevention. By taking preventive measures and seeking appropriate treatment when necessary, individuals can enjoy outdoor activities with minimal risk of developing grass rash. If symptoms persist or worsen, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for ensuring proper care and preventing complications. With the right approach, grass rash can be effectively managed, allowing for a more comfortable and enjoyable outdoor experience.
[inline_related_posts title=”You Might Be Interested In” title_align=”left” style=”list” number=”6″ align=”none” ids=”10137,10047,10036″ by=”categories” orderby=”rand” order=”DESC” hide_thumb=”no” thumb_right=”no” views=”no” date=”yes” grid_columns=”2″ post_type=”” tax=””]