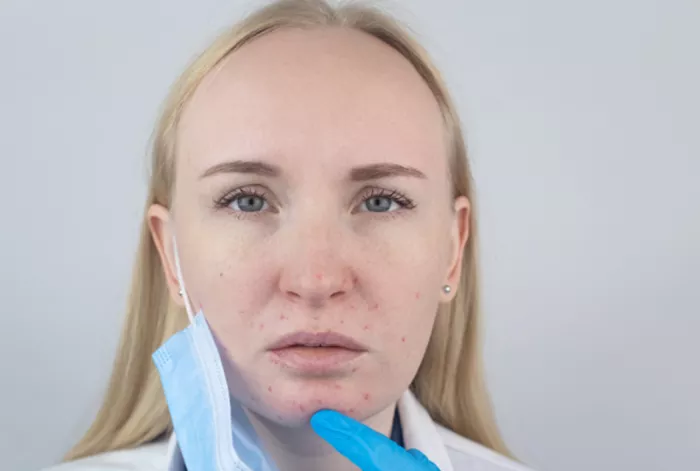
Wearing face masks has become a crucial part of daily life, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic. While masks are essential for preventing the spread of illness, some individuals may experience allergic reactions to certain mask materials or components. These reactions can manifest as itching, redness, rash, or even more severe symptoms. In this guide, we’ll explore the causes of allergic reactions to face masks and provide comprehensive strategies for treating and preventing them.
Understanding Allergic Reactions to Face Masks
Causes of Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions to face masks can occur due to various factors, including:
Mask Materials: Certain materials used in masks, such as latex, elastic, or adhesives, can trigger allergic reactions in sensitive individuals.
Chemicals: Some masks may contain chemicals or dyes that can irritate the skin and cause allergic reactions.
Fragrances: Fragrances added to masks for scent or antimicrobial purposes can also trigger allergic reactions in some people.
Sweat and Moisture: Prolonged wearing of masks can trap sweat and moisture against the skin, creating a breeding ground for bacteria and fungi that can cause irritation and allergic reactions.
Common Symptoms
Allergic reactions to face masks can manifest in various ways, including:
Itching: Persistent itching or tingling sensation on the skin, especially in areas covered by the mask.
Redness: Skin redness or inflammation, which may be localized or spread over a larger area.
Rash: Raised bumps, hives, or rash on the face, neck, or areas of mask contact.
Burning or Stinging: Sensation of burning or stinging on the skin, often accompanied by discomfort.
Swelling: Swelling of the face, lips, or eyelids, which can sometimes be severe and require medical attention.
Difficulty Breathing: In rare cases, allergic reactions to face masks can cause respiratory symptoms such as wheezing, coughing, or shortness of breath.
Treating Allergic Reactions to Face Masks
Immediate Steps
If you experience an allergic reaction to a face mask, take the following immediate steps:
Remove the Mask: Stop wearing the mask immediately to prevent further irritation and allow your skin to breathe.
Wash Your Face: Gently wash your face with a mild cleanser and lukewarm water to remove any residue from the mask.
Apply a Cold Compress: Use a cold compress or cool, damp cloth to soothe irritated skin and reduce inflammation.
Avoid Scratching: Resist the urge to scratch or rub the affected area, as this can worsen irritation and potentially lead to infection.
Topical Treatments
Several topical treatments can help alleviate symptoms of allergic reactions to face masks:
Hydrocortisone Cream: Over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream can reduce itching, redness, and inflammation caused by allergic reactions.
Calamine Lotion: Calamine lotion has soothing properties and can help relieve itching and irritation.
Aloe Vera Gel: Apply pure aloe vera gel to the affected area to soothe inflammation and promote healing.
Antihistamine Creams: Topical antihistamine creams can help reduce itching and allergic reactions on the skin.
Oral Medications
In some cases, oral medications may be necessary to manage more severe allergic reactions:
Antihistamines: Over-the-counter antihistamine medications such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or cetirizine (Zyrtec) can help relieve itching and reduce allergic symptoms.
Corticosteroids: In severe cases of allergic reactions, your doctor may prescribe oral corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
Moisturize and Protect
After treating the allergic reaction, it’s essential to keep the skin moisturized and protected:
Use a Gentle Moisturizer: Apply a gentle, fragrance-free moisturizer to the affected area to keep the skin hydrated and promote healing.
Choose Hypoallergenic Products: Use hypoallergenic skincare products that are free of fragrances, dyes, and other potential irritants.
Protective Barrier: Before wearing a mask again, apply a thin layer of petroleum jelly or zinc oxide ointment to create a protective barrier between the skin and the mask.
Seek Medical Advice
If your allergic reaction is severe or persistent, seek medical advice from a healthcare professional:
Consult a Dermatologist: A dermatologist can assess your symptoms, identify potential triggers, and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Allergy Testing: If you’re unsure what’s causing your allergic reaction, allergy testing may help identify specific allergens or irritants.
Prescription Medications: In some cases, prescription-strength medications or treatments may be necessary to manage severe allergic reactions.
Preventing Allergic Reactions to Face Masks
Prevention is key to avoiding allergic reactions to face masks. Here are some strategies to help prevent reactions:
Choose the Right Mask
Selecting the right mask can help minimize the risk of allergic reactions:
Hypoallergenic Masks: Look for masks labeled as hypoallergenic, which are less likely to contain common allergens or irritants.
Natural Materials: Choose masks made from natural materials such as cotton or silk, which are less likely to cause skin irritation.
Avoid Fragrances: Steer clear of masks with added fragrances, as these can trigger allergic reactions in sensitive individuals.
Test Before Use: If you’re unsure whether a mask will cause a reaction, perform a patch test by wearing the mask on a small area of skin for a short period to see if any irritation occurs.
Practice Good Skincare
Maintaining good skincare habits can help reduce the risk of allergic reactions:
Cleanse Your Skin: Wash your face with a mild cleanser before and after wearing a mask to remove dirt, oil, and sweat.
Moisturize Regularly: Keep your skin hydrated with a gentle, fragrance-free moisturizer to prevent dryness and irritation.
Avoid Harsh Products: Avoid using harsh skincare products or exfoliants that can strip the skin’s natural moisture barrier and increase sensitivity.
Take Regular Breaks
Give your skin a break from wearing masks to allow it to breathe and recover:
Take Mask-Free Breaks: Whenever possible, take short breaks from wearing a mask, especially if you’re in a safe and socially distanced environment.
Limit Wear Time: If you’re experiencing irritation or discomfort, limit the amount of time you wear a mask and remove it when necessary.
Practice Proper Mask Hygiene
Proper mask hygiene can help prevent bacterial or fungal growth that can contribute to allergic reactions:
Wash Your Mask Regularly: Wash reusable masks after each use with soap and hot water, or follow manufacturer instructions for cleaning.
Rotate Masks: Use multiple masks and rotate them regularly to allow time for washing and drying between uses.
Avoid Moisture Buildup: Change your mask if it becomes damp or wet from sweat or moisture to prevent bacterial growth.
Consider Alternative Mask Options
If you continue to experience allergic reactions despite taking preventive measures, consider alternative mask options:
Different Materials: Try masks made from different materials or fabrics to see if you react differently to alternative options.
Mask Accessories: Consider using mask accessories such as mask liners or barrier creams to create a protective barrier between your skin and the mask.
Consult a Specialist: If you have a known allergy or sensitivity, consult with an allergist or dermatologist for personalized recommendations on mask options.
Conclusion
Allergic reactions to face masks can be uncomfortable and distressing, but with the right treatment and prevention strategies, you can manage symptoms effectively and minimize the risk of future reactions. By understanding the causes of allergic reactions, knowing how to treat them, and taking proactive steps to prevent them, you can ensure a safer and more comfortable mask-wearing experience. If you experience severe or persistent allergic reactions, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice from a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment. With proper care and attention, you can protect your skin and maintain your health while wearing a face mask.
[inline_related_posts title=”You Might Be Interested In” title_align=”left” style=”list” number=”6″ align=”none” ids=”9641,9638,9591″ by=”categories” orderby=”rand” order=”DESC” hide_thumb=”no” thumb_right=”no” views=”no” date=”yes” grid_columns=”2″ post_type=”” tax=””]