Skin allergies are common afflictions that affect millions of people worldwide. Characterized by redness, itching, and sometimes swelling, these reactions can be triggered by a variety of factors, including environmental irritants, food, medications, and insect stings. While often considered a minor nuisance, neglecting to treat skin allergies can lead to serious health issues and a diminished quality of life. This article explores what happens when skin allergies are not treated, detailing the risks and complications that can arise from such negligence.
Understanding Skin Allergies
Before delving into the consequences of untreated skin allergies, it is important to understand what they are and how they manifest.
Types of Skin Allergies
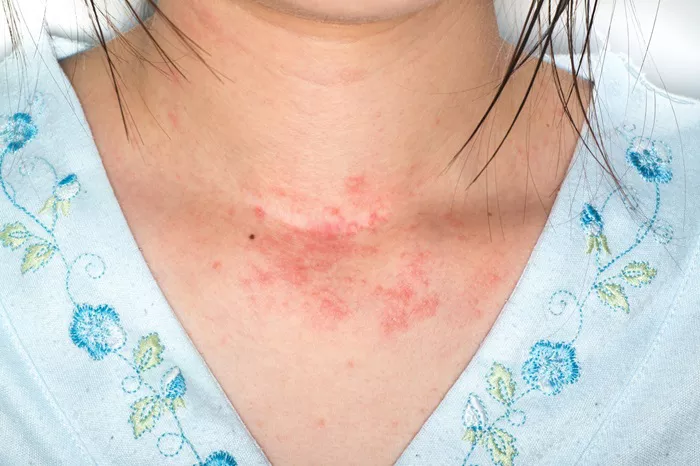
Contact Dermatitis: Occurs when the skin comes into contact with an allergen (like nickel or latex) or an irritant (such as poison ivy).
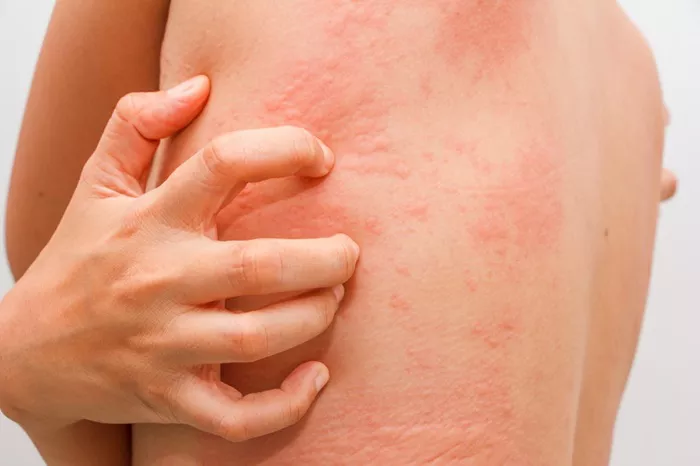
Urticaria (Hives): Appears as sudden outbreaks of swollen, pale red bumps, patches, or welts on the skin.
Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema): A chronic skin condition that makes the skin red, inflamed, and itchy.
Symptoms of Skin Allergies
Common symptoms include redness, itching, swelling, and the formation of vesicles or blisters. In some cases, symptoms may appear immediately after exposure to an allergen, while in others, they may take longer to develop.
Immediate and Long-Term Risks of Untreated Skin Allergies
Failing to manage and treat skin allergies properly can lead to a variety of complications, affecting more than just the skin.
Persistent Discomfort and Itchiness
The most immediate consequence of an untreated skin allergy is persistent discomfort or itchiness. Chronic itchiness can lead to scratching, which aggravates the skin further and can inhibit daily activities and sleep.
Secondary Skin Infections
Persistent scratching can cause breaks in the skin, leaving it vulnerable to infections. Bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus, can enter through these breaks and cause painful, sometimes serious, infections.
Scarring and Skin Discoloration
Repeated scratching or rubbing of the affected area can also lead to permanent changes in skin texture and color. Thickening of the skin (lichenification) and hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation are common results of chronic skin allergies.
Impact on Quality of Life
Chronic skin conditions like eczema can significantly impact quality of life, leading to sleep disturbances, reduced self-esteem, and social withdrawal. The constant discomfort can also impair concentration and daily functioning.
Complications from Specific Types of Skin Allergies
Different types of skin allergies have their own sets of potential complications if not properly managed.
Atopic Dermatitis
Eczema Herpeticum: A serious complication where herpes simplex virus infects eczema-damaged skin, potentially resulting in widespread infection.
Eye Complications: Chronic rubbing of itchy skin around the eyes can lead to eye conditions such as conjunctivitis or keratoconus.
Contact Dermatitis
Chronic Skin Changes: Ongoing exposure to the irritant or allergen can lead to chronic skin dermatitis, which may be harder to treat and could become more susceptible to secondary infections.
Urticaria
Anaphylaxis: In severe cases, hives can be part of a broader allergic reaction that includes anaphylaxis, a potentially life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Diagnosing and Treating Skin Allergies
Proper diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing the symptoms of skin allergies and preventing long-term consequences.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis typically involves a detailed medical history and physical examination. Allergy tests (like patch tests or skin prick tests) might be conducted to identify specific allergens.
Treatment Options
Avoidance of Triggers: Identifying and avoiding allergens or irritants is critical in preventing allergic reactions.
Topical Treatments: Steroid creams and emollients are commonly used to reduce inflammation and moisturize the skin.
Antihistamines: These medications can help control itching and swelling.
Immunotherapy: In cases where specific allergens are identified, allergy shots might be recommended to decrease sensitivity to these allergens.
Prevention Strategies
In addition to treatment, implementing effective prevention strategies is key to managing skin allergies.
Regular Skin Care
Maintaining a regular skin care regimen can help protect the skin barrier and prevent flare-ups. This includes using hypoallergenic products and moisturizing regularly.
Environmental Controls
Reducing exposure to known allergens in the home and work environment can prevent allergic reactions. This may involve using air purifiers, avoiding certain fabrics, and maintaining a clean living space.
Education and Awareness
Educating patients and caregivers about the triggers and proper management of skin allergies is fundamental. Understanding when to seek medical help is also crucial in preventing complications.
Conclusion: The Importance of Addressing Skin Allergies
While they may seem trivial, untreated skin allergies can lead to severe complications and significantly impact health and quality of life. Recognizing the symptoms early and consulting with healthcare professionals for appropriate treatment and management strategies can mitigate these risks. Through a combination of medical treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and preventive care, individuals with skin allergies can lead healthier, more comfortable lives.
[inline_related_posts title=”You Might Be Interested In” title_align=”left” style=”list” number=”6″ align=”none” ids=”8296,8292,8287″ by=”categories” orderby=”rand” order=”DESC” hide_thumb=”no” thumb_right=”no” views=”no” date=”yes” grid_columns=”2″ post_type=”” tax=””]