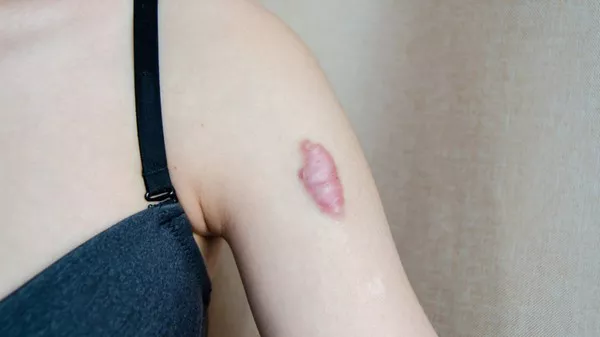
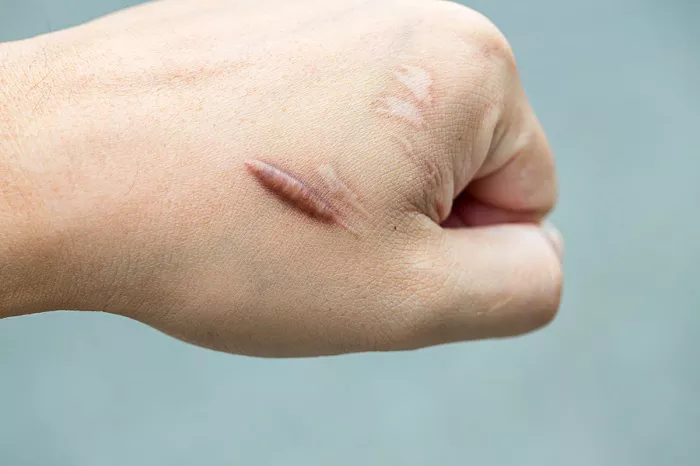
Dealing with burns and scars can be a challenging journey, both physically and emotionally. In the pursuit of effective remedies, Vitamin E has emerged as a popular option. This article delves into the multifaceted role of Vitamin E in the context of burns and scars, exploring its potential benefits, application methods, and considerations for optimal results. From its antioxidant properties to its impact on collagen formation, understanding Vitamin E’s therapeutic potential is a key step in navigating the path to scar healing and improved skin health.
The Role of Vitamin E in Skin Health
Vitamin E, a fat-soluble antioxidant, plays a crucial role in maintaining skin health. As a potent scavenger of free radicals, Vitamin E helps protect skin cells from oxidative damage caused by environmental factors such as UV rays and pollution. While its general role in skin health is well-established, its specific benefits in the context of burns and scars make it a subject of interest for those seeking natural and supportive remedies.
Antioxidant Power
When the skin experiences burns, whether from heat, chemicals, or radiation, the resulting damage triggers an inflammatory response that generates free radicals. These highly reactive molecules can exacerbate tissue damage and hinder the healing process. Vitamin E’s antioxidant properties come into play by neutralizing these free radicals, potentially minimizing oxidative stress and supporting the skin’s natural healing mechanisms.
Research suggests that applying Vitamin E topically can enhance the antioxidant defense system of the skin, particularly when it comes to burns. By reducing oxidative stress, Vitamin E may contribute to a more favorable environment for the healing of burn injuries.
Collagen Synthesis
Collagen, a structural protein in the skin, plays a pivotal role in wound healing and scar formation. Vitamin E is believed to influence collagen synthesis, which is crucial for the remodeling of damaged skin tissue. By promoting collagen production, Vitamin E may contribute to the formation of a more organized and uniform scar tissue, potentially reducing the visibility of scars.
In the context of burns, where the depth and severity of the injury can vary, supporting the skin’s natural ability to produce collagen becomes paramount. While Vitamin E alone may not completely eliminate scars, its role in collagen synthesis positions it as a valuable ally in the scar reduction process.
Topical Application of Vitamin E
The most common method of using Vitamin E for burns and scars is through topical application. Vitamin E oil or creams containing Vitamin E are readily available over the counter and are often touted for their skin-nourishing properties. However, it’s essential to approach topical Vitamin E with a nuanced understanding of its benefits and potential risks.
Benefits of Topical Vitamin E:
Moisturization and Hydration: Vitamin E is known for its moisturizing properties, making it beneficial for dry or damaged skin. Properly hydrated skin is more conducive to the healing process, especially in the case of burns.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Inflammation is a natural response to burns, but excessive inflammation can impede the healing process. Vitamin E’s anti-inflammatory properties may help mitigate excessive inflammation and contribute to a more controlled healing environment.
Scar Reduction Potential: The potential of Vitamin E to influence collagen synthesis makes it a candidate for scar reduction. Applying Vitamin E topically to scars may contribute to a more favorable texture and appearance over time.
Risks and Considerations:
Skin Sensitivity: Some individuals may be sensitive to Vitamin E, experiencing skin irritation or allergic reactions. Conducting a patch test before widespread application is advisable, especially for those with a history of skin sensitivity.
Effectiveness Variability: The effectiveness of topical Vitamin E can vary among individuals. Factors such as the type and severity of the burn, skin type, and overall health can influence how the skin responds to Vitamin E.
Potential for Contact Dermatitis: In some cases, topical Vitamin E may cause contact dermatitis, characterized by redness, itching, or a rash. This reaction is more likely when using pure Vitamin E oil or high concentrations of Vitamin E in skincare products.
DIY Vitamin E Remedies
Given the popularity of Vitamin E in scar and burn care, many individuals explore do-it-yourself (DIY) remedies. These can include creating homemade ointments or masks using Vitamin E-rich ingredients. While the intention is often to harness the benefits of Vitamin E in a natural form, it’s crucial to approach DIY applications with caution.
DIY Vitamin E Remedies:
Vitamin E Oil Application: Applying Vitamin E oil directly to the affected area is a common DIY approach. However, it’s essential to ensure the purity and quality of the oil, as some formulations may contain additional ingredients that could cause adverse reactions.
Vitamin E and Aloe Vera Combo: Mixing Vitamin E oil with aloe vera gel is a popular combination for burns and scars. Aloe vera is known for its soothing properties, and when combined with Vitamin E, it creates a hydrating and potentially beneficial concoction.
Vitamin E and Honey Mask: Creating a mask by combining Vitamin E oil with honey is another DIY remedy. Honey is recognized for its antimicrobial properties and can complement Vitamin E in supporting the healing process.
Considerations for DIY Applications:
Ingredient Quality: When creating DIY remedies, the quality of ingredients, particularly Vitamin E oil, is paramount. Using pure, high-quality Vitamin E oil minimizes the risk of adverse reactions.
Skin Sensitivity Testing: Before applying DIY remedies to larger areas, conducting a patch test on a small, inconspicuous area helps assess how the skin responds. This is especially crucial for individuals with sensitive skin.
Consistency and Patience: DIY applications may require consistent and prolonged use to observe noticeable results. Patience is key, and individuals should discontinue use if any adverse reactions occur.
Supplemental Vitamin E
While much of the focus on Vitamin E in burn and scar care revolves around topical applications, the potential benefits of oral supplementation should not be overlooked. Consuming Vitamin E through dietary sources or supplements provides the body with the necessary building blocks for skin health from within.
Vitamin E-Rich Foods:
Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, sunflower seeds, and hazelnuts are rich sources of Vitamin E. Including these in the diet contributes not only to Vitamin E intake but also to other essential nutrients.
Vegetable Oils: Sunflower oil, wheat germ oil, and safflower oil are examples of vegetable oils high in Vitamin E. Using these oils in cooking or as dressings supports overall skin health.
Leafy Greens: Spinach, Swiss chard, and kale are leafy greens with significant Vitamin E content. Incorporating these into meals enhances the overall antioxidant profile of the diet.
Oral Vitamin E Supplements:
Considerations for Dosage: The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for Vitamin E varies based on factors such as age, sex, and life stage. It’s essential to adhere to recommended dosages, as excessive Vitamin E intake can lead to adverse effects.
Consultation with Healthcare Professionals: Before initiating oral Vitamin E supplementation, consulting with a healthcare professional is advisable. They can assess individual health status and provide guidance on appropriate dosage and potential interactions with other medications.
Comprehensive Nutrition Approach: While Vitamin E is a valuable component of skin health, it’s essential to adopt a comprehensive approach to nutrition. A diet rich in diverse antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals supports overall well-being and skin resilience.
Scientific Evidence and Controversies: Navigating the Landscape
The scientific literature on the efficacy of Vitamin E in scar and burn care is both extensive and, at times, controversial. While some studies support the positive impact of Vitamin E on scar reduction and wound healing, others suggest more nuanced outcomes. Understanding the existing evidence helps individuals make informed decisions about incorporating Vitamin E into their skincare routines.
Scientific Support for Vitamin E:
Clinical Studies on Scars: Some clinical studies suggest that topical application of Vitamin E may be beneficial in improving scar texture and appearance. However, the results can vary, and individual factors may influence the outcomes.
Wound Healing Investigations: Research on the role of Vitamin E in wound healing indicates its potential in promoting tissue repair. Its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties contribute to a conducive environment for the healing process.
Controversies and Contradictions:
Limited Consensus on Effectiveness: Despite positive findings in certain studies, there is not a unanimous consensus on the effectiveness of Vitamin E in scar and burn care. Factors such as study design, participant characteristics, and scar types contribute to the variability in results.
Risk of Adverse Effects: Some studies have raised concerns about the potential for adverse effects, particularly with high doses of Vitamin E. These effects may include skin irritation, allergic reactions, or interference with the natural healing process.
Individual Considerations
Navigating the landscape of Vitamin E for burns and scars requires a personalized approach that takes into account individual factors, the nature of the injury, and overall health. Understanding that responses to Vitamin E can vary, individuals can tailor their use of Vitamin E to address specific needs.
Considerations for Tailoring Vitamin E Use:
Type and Severity of the Burn: Different burns, whether first-degree, second-degree, or more severe, may respond differently to Vitamin E. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help determine the most appropriate approach based on the specific burn type.
Skin Type and Sensitivity: Individuals with sensitive skin may need to exercise extra caution when using Vitamin E topically. Conducting a patch test and starting with lower concentrations can help minimize the risk of adverse reactions.
Age of the Scar: The age of the scar can influence its responsiveness to treatment. Newer scars may be more amenable to intervention, while older scars may be less responsive. Consistent and prolonged use may be necessary for observable results.
Combination Approaches: Combining Vitamin E with other beneficial ingredients, such as aloe vera or honey, may enhance its overall effectiveness. Experimenting with combination approaches can be a strategy for optimizing results.
Professional Guidance
While Vitamin E holds promise in scar and burn care, seeking professional guidance is crucial, especially in cases of severe burns or persistent skin issues. Dermatologists and healthcare providers can offer tailored advice, assess the specific needs of the individual, and provide recommendations based on the latest scientific evidence.
When to Consult a Professional:
Severe Burns: For severe burns, especially those requiring medical attention or intervention, consulting with a healthcare professional is essential. They can guide the initial stages of care and offer insights into long-term scar management.
Persistent Skin Issues: If skin issues persist despite the use of Vitamin E or if adverse reactions occur, seeking the expertise of a dermatologist is advisable. They can conduct a comprehensive evaluation and recommend appropriate adjustments to the skincare routine.
Individualized Treatment Plans: Dermatologists can develop individualized treatment plans that may include a combination of medical interventions, topical treatments, and lifestyle recommendations. This comprehensive approach addresses the unique characteristics of the individual’s skin and scars.
Conclusion
The journey of managing burns and scars is a multifaceted one, and Vitamin E emerges as a versatile ally in this pursuit. From its antioxidant prowess to its potential impact on collagen synthesis, Vitamin E offers a range of benefits that individuals can explore in their skincare routines.
However, it’s crucial to approach Vitamin E with a nuanced understanding, recognizing that its effectiveness can vary among individuals and across different types of scars. Whether applied topically, incorporated into DIY remedies, or consumed through dietary sources, the key lies in consistency, patience, and a commitment to overall skin health.
In the realm of burns and scars, Vitamin E stands as a testament to the intricate interplay between nutrition, skincare, and the body’s innate healing mechanisms. By navigating this landscape with informed choices and professional guidance when needed, individuals can foster skin resilience, promote scar reduction, and embark on a path toward renewed skin confidence.
[inline_related_posts title=”You Might Be Interested In” title_align=”left” style=”list” number=”6″ align=”none” ids=”3224,3166,3164″ by=”categories” orderby=”rand” order=”DESC” hide_thumb=”no” thumb_right=”no” views=”no” date=”yes” grid_columns=”2″ post_type=”” tax=””]