Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD), often referred to as seasonal depression, affects millions of people worldwide. This condition typically occurs during the fall and winter months when sunlight exposure is limited, leading to a drop in mood and overall well-being. One of the key factors in managing and potentially alleviating the symptoms of SAD is ensuring adequate levels of Vitamin D. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the importance of Vitamin D, which vitamin D for seasonal depression, and how it can be effectively used to combat seasonal depression.
Understanding Seasonal Affective Disorder
What is Seasonal Affective Disorder?
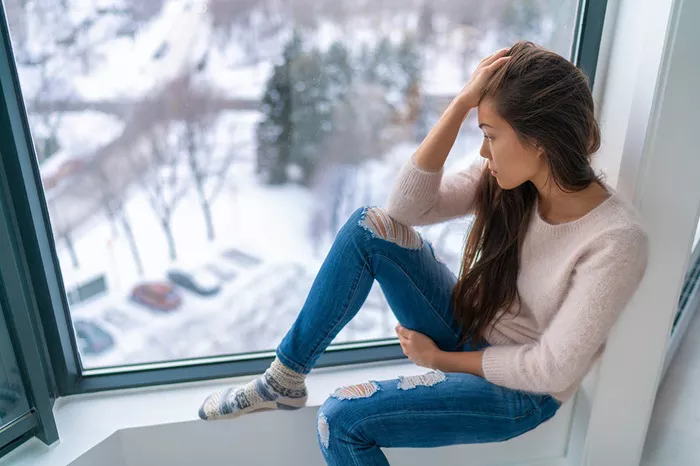
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) is a type of depression that occurs at specific times of the year, usually in the fall and winter. It is characterized by symptoms such as fatigue, depression, hopelessness, and social withdrawal. The primary cause of SAD is believed to be a lack of sunlight, which disrupts the body’s internal clock, or circadian rhythm, and leads to a drop in serotonin levels.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Common symptoms of SAD include:
- Persistent low mood
- Loss of interest in activities once enjoyed
- Irritability
- Feelings of despair, guilt, and worthlessness
- Lethargy and sleep problems
- Changes in appetite, particularly craving carbohydrates
Diagnosing SAD involves evaluating the timing and pattern of depressive episodes. A healthcare provider will typically look for a history of depression that occurs at specific times of the year and remits in the spring or summer.
The Role of Vitamin D
What is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D, also known as the “sunshine vitamin,” is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays a critical role in bone health, immune function, and mood regulation. The body synthesizes Vitamin D when the skin is exposed to sunlight, specifically ultraviolet B (UVB) rays. It can also be obtained through certain foods and supplements.
Vitamin D and Mood Regulation
Research has shown that Vitamin D receptors are present in areas of the brain that are linked to depression. Vitamin D is thought to influence the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that affects mood. Low levels of serotonin are associated with depression, and increasing serotonin levels can improve mood and alleviate depressive symptoms.
See Also: What Vitamins Can I Take with Folic Acid?
Evidence Linking Vitamin D and SAD
Several studies have investigated the relationship between Vitamin D and SAD. A study published in the Journal of Affective Disorders found that individuals with SAD had lower levels of Vitamin D compared to those without the condition. Supplementing with Vitamin D has been shown to improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression, making it a potential treatment for SAD.
Types of Vitamin D
Vitamin D2 vs. Vitamin D3
There are two main forms of Vitamin D: Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol).
Vitamin D2 (Ergocalciferol): This form of Vitamin D is derived from plant sources and fortified foods. It is not as effective as Vitamin D3 in raising blood levels of Vitamin D.
Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol): This form is produced in the skin in response to sunlight and is found in animal-based foods. It is more effective than Vitamin D2 at increasing and maintaining adequate levels of Vitamin D in the body.
Which Form is Better for Seasonal Depression?
For managing seasonal depression, Vitamin D3 is generally recommended over Vitamin D2 due to its superior ability to raise and maintain Vitamin D levels. Studies have shown that Vitamin D3 is more effective in treating and preventing Vitamin D deficiency, which is crucial for individuals with SAD.
Sources of Vitamin D
Sunlight
The most natural way to obtain Vitamin D is through sunlight exposure. Spending time outdoors, particularly during midday when the sun’s rays are strongest, can help increase Vitamin D levels. However, during the fall and winter months, sunlight exposure is often insufficient, especially in higher latitudes.
Food Sources
Certain foods are rich in Vitamin D, including:
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna)
- Cod liver oil
- Fortified dairy products (milk, yogurt)
- Fortified cereals
- Egg yolks
Supplements
When sunlight and dietary sources are inadequate, Vitamin D supplements can be an effective way to ensure sufficient intake. Vitamin D3 supplements are widely available and come in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and liquid drops.
How to Use Vitamin D for Seasonal Depression
Recommended Dosage
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for Vitamin D varies depending on age, sex, and life stage. For adults, the RDA is typically 600-800 IU (International Units) per day. However, for individuals with SAD, higher doses may be required to achieve optimal blood levels. Consulting with a healthcare provider is essential to determine the appropriate dosage.
Monitoring Vitamin D Levels
Regular monitoring of blood levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D is important for individuals taking Vitamin D supplements. This helps ensure that levels are within the optimal range (30-50 ng/mL) and allows for adjustments in dosage if necessary.
Safety and Potential Side Effects
Vitamin D is generally safe when taken at recommended doses. However, excessive intake can lead to toxicity, with symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, weakness, and kidney damage. It is crucial to follow the guidance of a healthcare provider when using Vitamin D supplements.
Additional Strategies to Manage Seasonal Depression
Light Therapy
Light therapy, or phototherapy, involves exposure to bright light that mimics natural sunlight. It is one of the most effective treatments for SAD and can be used in conjunction with Vitamin D supplementation.
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity can help improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression. Activities such as walking, running, and yoga can be beneficial.
Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins supports overall health and well-being. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish and flaxseeds, have also been shown to improve mood.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a form of psychotherapy that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors. It has been shown to be effective in treating SAD.
Conclusion
Seasonal Affective Disorder is a debilitating condition that can significantly impact quality of life. Ensuring adequate levels of Vitamin D, particularly through the use of Vitamin D3 supplements, is a crucial strategy in managing and alleviating the symptoms of SAD. Along with other treatments such as light therapy, physical activity, and a healthy diet, Vitamin D can play a vital role in improving mood and overall well-being during the challenging fall and winter months. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure safety and efficacy.
[inline_related_posts title=”You Might Be Interested In” title_align=”left” style=”list” number=”6″ align=”none” ids=”10569,10493,10479″ by=”categories” orderby=”rand” order=”DESC” hide_thumb=”no” thumb_right=”no” views=”no” date=”yes” grid_columns=”2″ post_type=”” tax=””]